1. MapReduce概述
MapReduce是一种分布式计算模型,由google提出,主要用于搜索领域,解决海量数据的计算问题。
mapr由两个阶段组成:MAP和Reduce,用户只需要实现map()和reduce()两个函数,即可实现分布式计算,非常简单。
这两个函数的形参是key、value对,表示函数的输入信息。
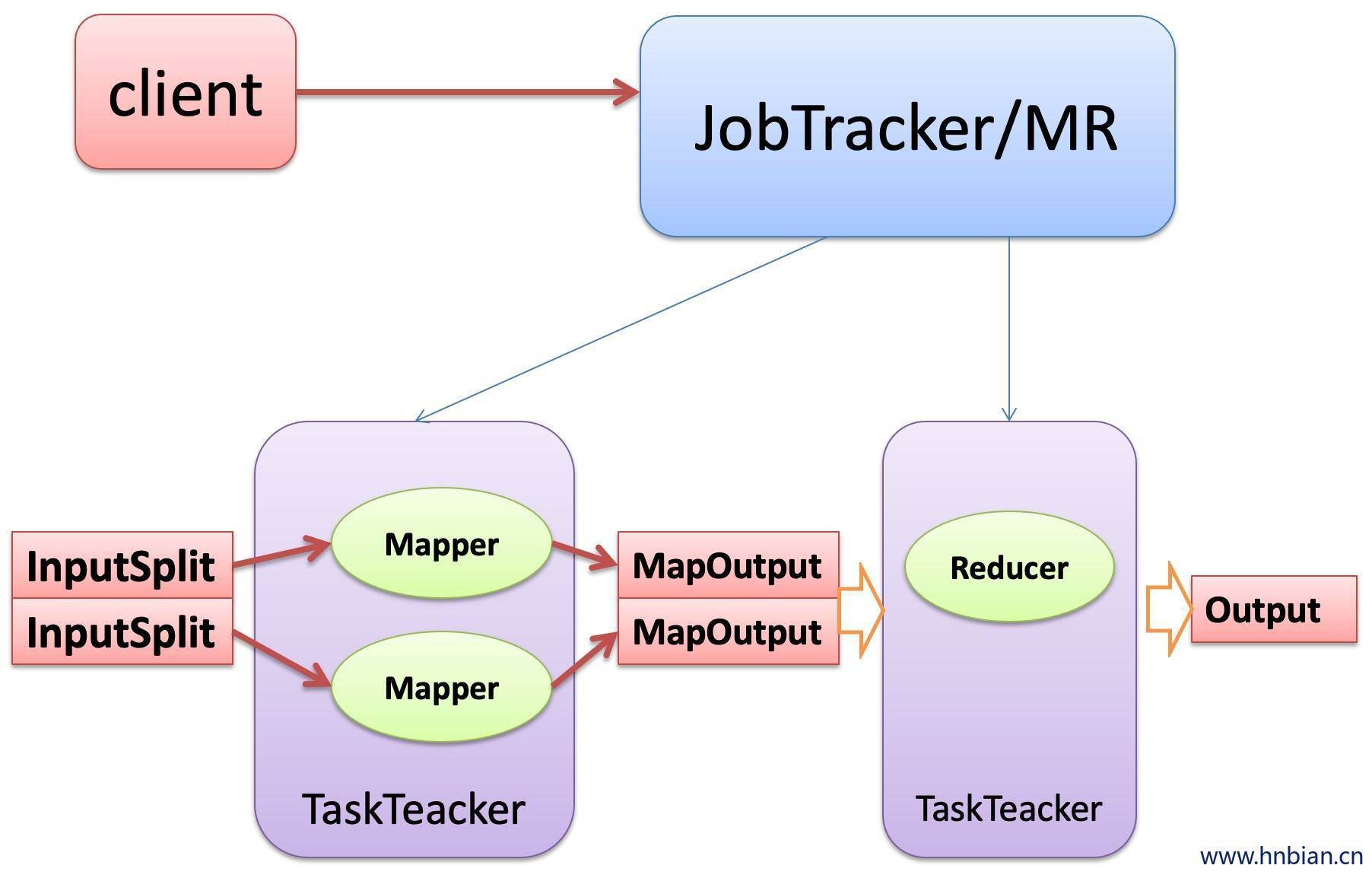
2. MapReduce的原理
要实现MapReduce模型 需要重写map与reduce方法。
map的输入 k1 V1 ,map的输出也是reduce的输入 K2V2 ,reduce的输出 K3V3
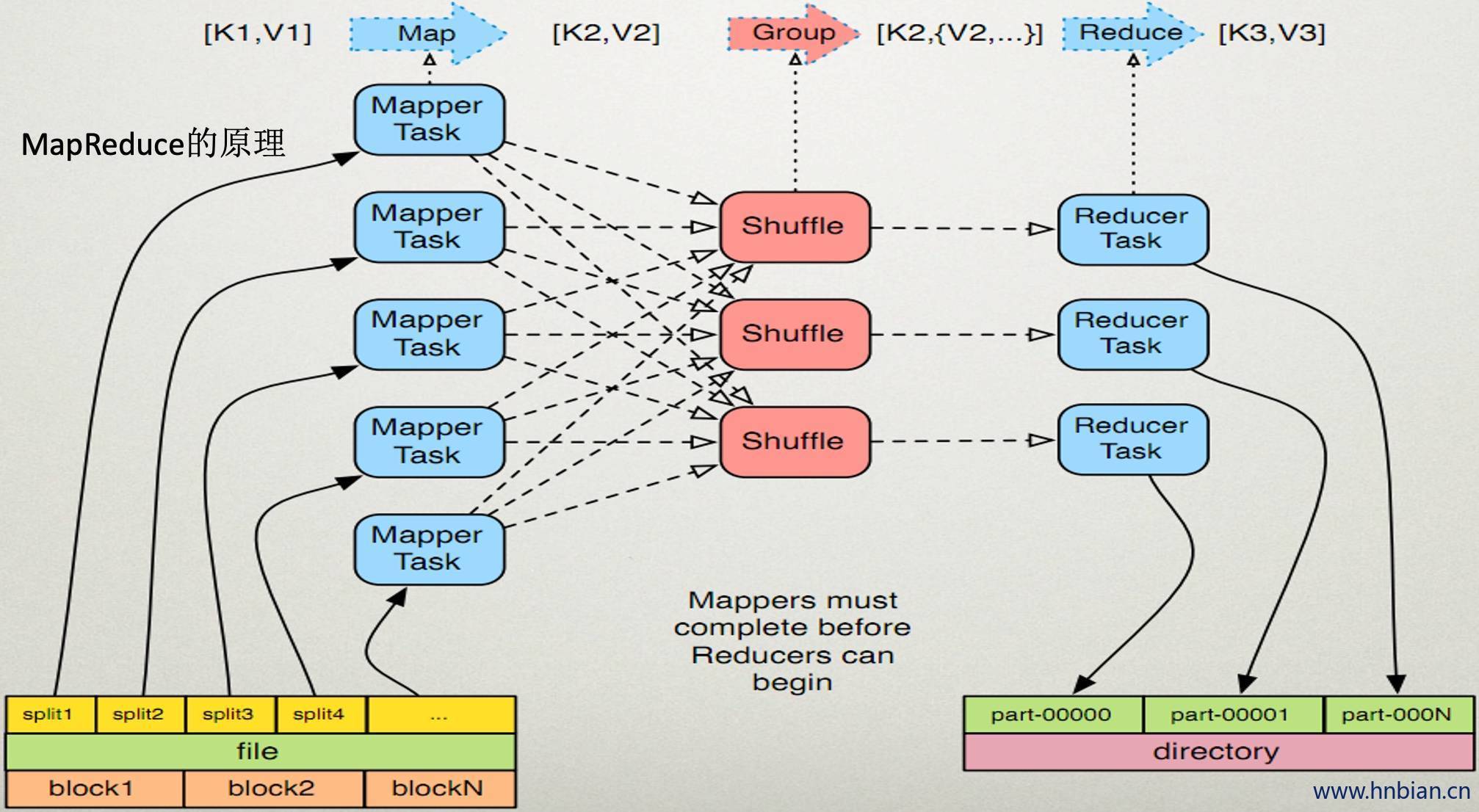
2.1map任务处理
读取输入文件内容,解析成key、value对。对输入文件的每一行,解析成key、value对。每一个键值对调用一次map函数
写自己的逻辑,对输入的key、value处理,转换成新的key、value输出。
对输出的key、value进行分区
对不同分区的数据,按照key进行排序、分组。相同key的value放到一个集合中//。
(可选)分组后的数据进行归约。
2.2 reduce任务处理
对于多个map任务的输出,按照不同的分区,通过网络copy到不同的reduce节点
对多个map任务的输出进行合并、排序。写reduce函数自己的逻辑,对输入的key、value处理,转换成新的key、value输出。
把reduce的输出保存到文件中。
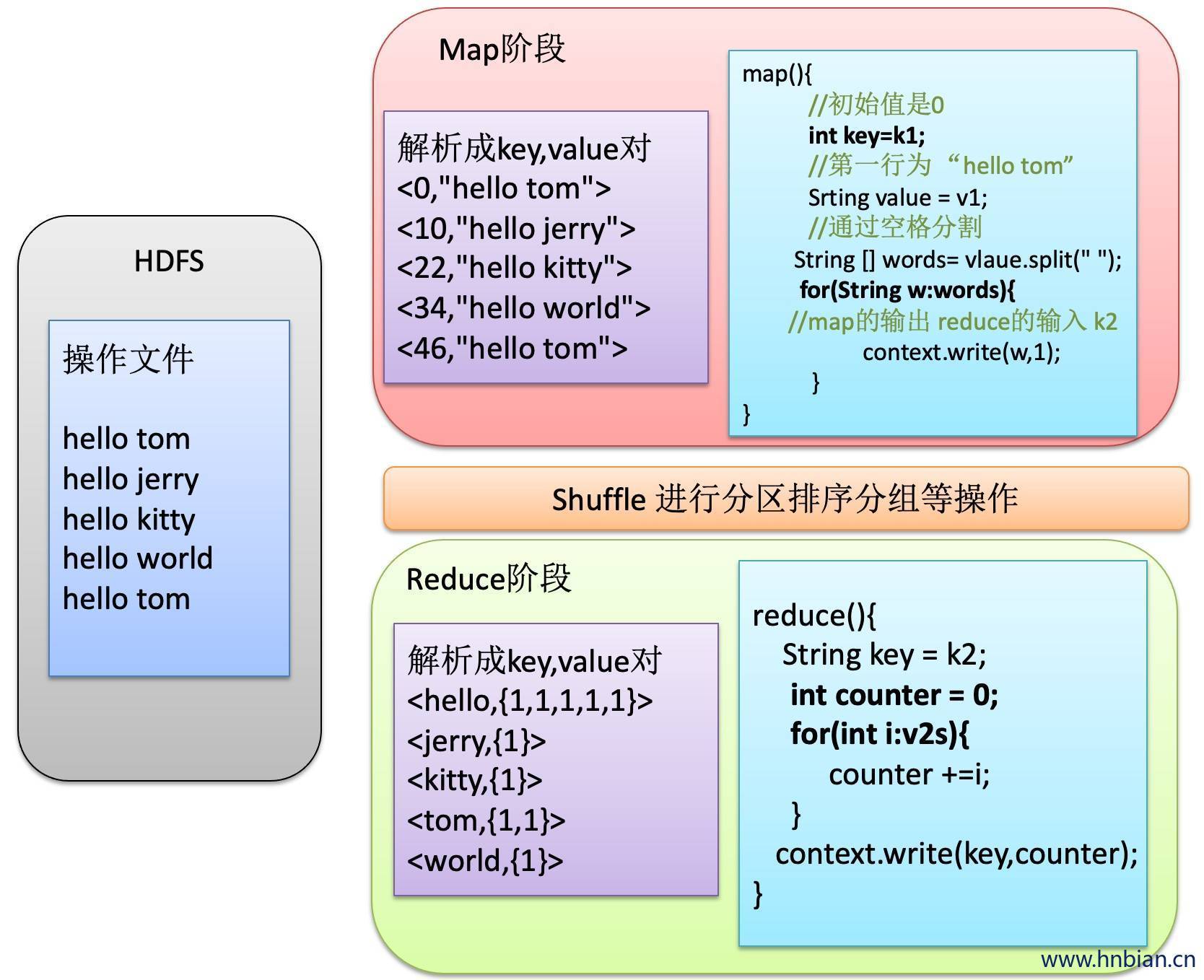
3. MapReduce 代码示例
分析具体的业务逻辑
确定输入输出的数据的样式
自定义一个类,这个类要继承mapper类 重写map()方法在map方法里实现具体逻辑,然后将新的key,value输出
自己定义一个类,这个类要继承reduce类,重写reduce()方法,在reduce方法里实现自己的逻辑
将自定义的mapper与reducer通过job对象组装起来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
|
package mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
public class WcMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String words[] = line.split(" ");
for(String w:words){
context.write(new Text(w), new LongWritable(1));
}
}
}
package mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
public class WcReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<LongWritable> v2s,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Text k3 = k2;
long conter = 0;
for(LongWritable i:v2s){
conter +=i.get();
}
context.write(k3,new LongWritable(conter));
}
}
package mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(WcMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/words.txt"));
job.setReducerClass(WcReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/wcOunt"));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
|
打好jar文件之后
在Client运行hadoop -jar 实际上是运行MapReduce的main方法,要构建一个job, 然后job将jar提交到hadoop集群。
- job里面还持有一个jobClient,任务先给jobClient,jobClient持有rm的代理对象与rm进行通信,rm先给jobclient一个jobid 又给jobclient一个存放jar的位置。
- jobclient将返jar要存放的位置作为前缀,jobid作为后缀拼接起来作为路径,将jar文件存到hdfs中。(通过FileSystem写十份)
将作业提交给rm,提交作业的描述信息(作业id,jar位置等等)
rm接收到消息之后,将信息初始化,然后将作业存放到调度器里面。
决定启动多少mapper 与多少reducer(由数据量决定)
nm通过心跳机制向rm领取任务
nm领取到任务之后到hdfs中下载jar文件
下载完jar之后,nm启动另外的java进程,在进程中之后map或reduce
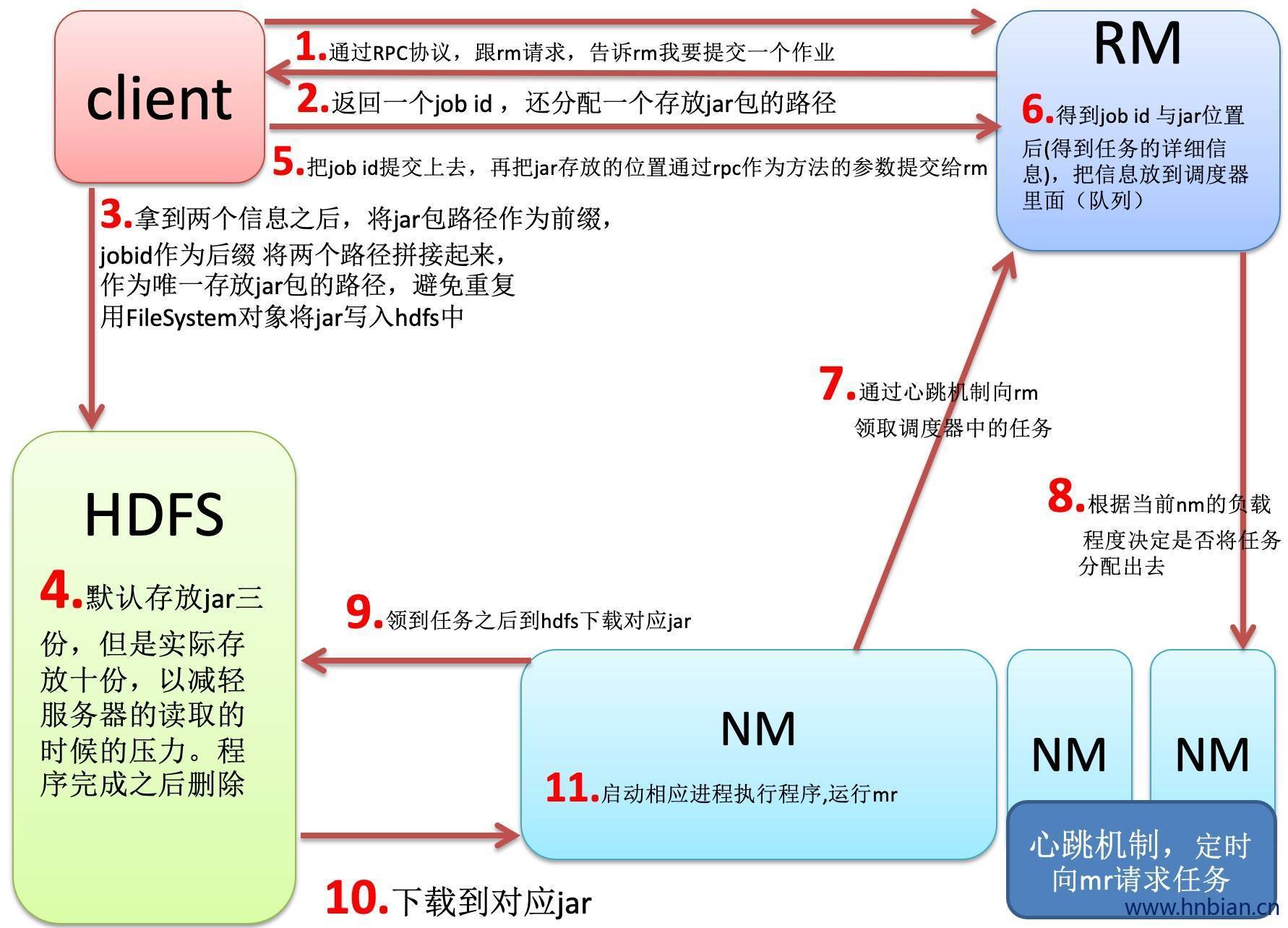
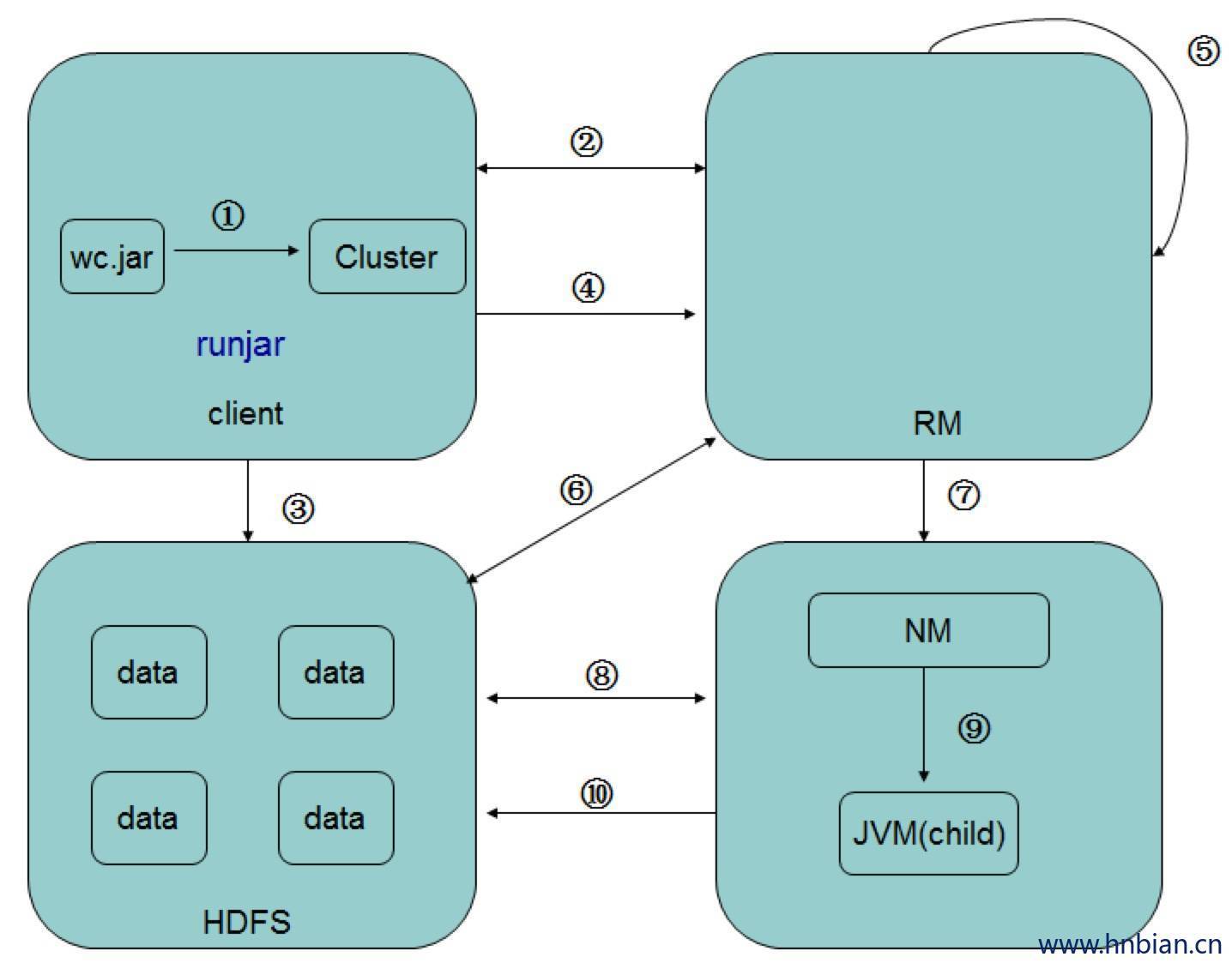
4. MapReduce中的角色
- jobClient:提交作业
- RM(ResourceManager):初始化作业、分配作业,nm与其进行通信,协调监控整个作业
- NM(NodeManager):定期与rm通信,执行map和reduce任务
- Hdfs:保存作业的数据、配置、jar包、结果。
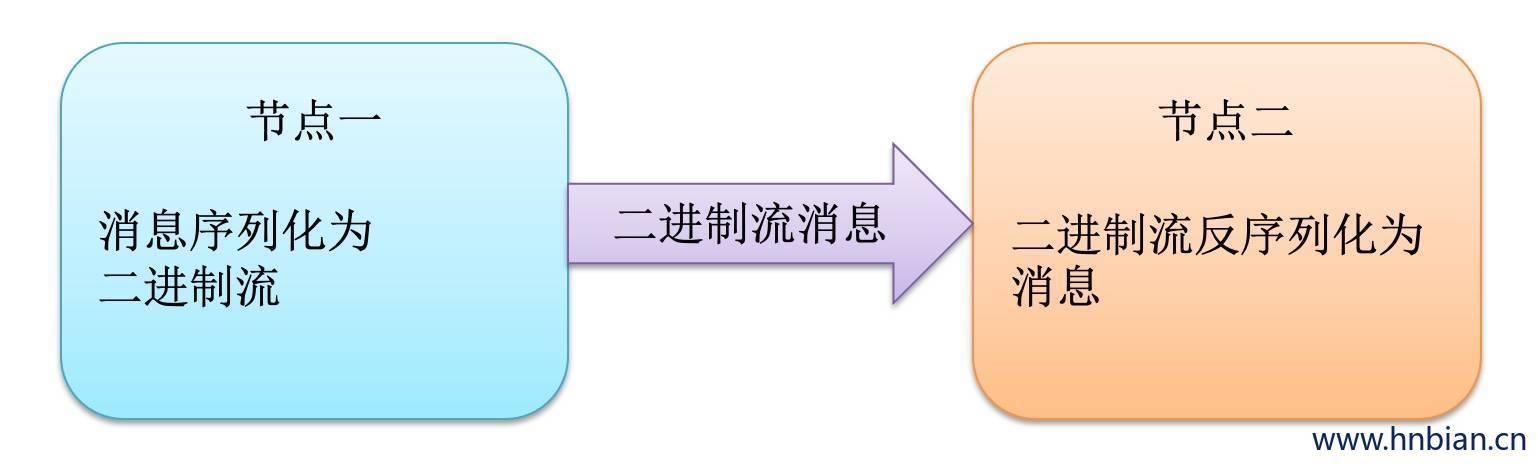
5. 序列化概念
- 序列化(Serialization)是指把结构化对象转换为字节流。
- 反序列化(Deserizlization)是序列化的逆过程。即把字节流转回结构化对象
- Java序列化(java.io.Serializable)
5.1 hadoop序列化的特点
序列化格式特点
- 紧凑:高效使用存储空间
- 快速:读写数据的额外开销小
- 可扩展:可透明地读取老格式的数据
- 互操作:支持多语言的交互
hadoop的序列化格式 Writable
5.2 hadoop序列化的作用
- 序列化在分布式环境中的两大作用:进程间通信,永久储存。
- hadoop节点之间通信
5.3 常用的Writable实现类
Text一般认为它等价于Java.lang.String的Writable。针对UTF-8序列。
例:Text t = new Text(“text”);
IntWritable one = new intWritable(1);
5.4 Writable接口
Writable接口,是根据DataInput 和 DataOutput 实现的简单,有效的序列化对象。
MR的任意key和value必须实现Writable接口
MR的任意key必须实现WritableComparable接口
| java基本类型 |
Writable |
序列化大小(字节) |
| boolean |
BooleanWritable |
1 |
| byte |
ByteWritable |
1 |
| int |
IntWritable |
4 |
|
vintWritable |
1~5 |
| float |
FloatWritable |
4 |
| long |
LongWritable |
9 |
|
vlongWritable |
1~9 |
| double |
DoubleWritable |
8 |
5.5 Writable
- write是把每个对象序列化到输出流
- readFields是把输入流字节反序列化
- 在执行MapReduce之前,原始数据被分割成若干split,每个split作为一个map任务的输入,在map执行过程中split会被分解成一个个记录(key-value对),map会依次处理每一个记录
- FileInputFormat只划分比HDFS block大的文件,所以FileInputFormat划分的结果是这个文件或者是这个文件中的一部分
- 如果一个文件的大小比block小,将不会划分,这也是Hadoop处理大文件的效率要比处理很多小文件的效率高的原因。
- 当Hadoop处理很多小文件(文件大小小于HDFS block大小)的时候,由于FileInputFormat 不会对小文件进行划分,所以每一个小文件都会被当做一个split并分配一个map任务,导致效率低下。
- 例如:一个G的文件,将会划分成8个128MB的split,并分配成8个map任务处理,而10000个100kb的文件会被10000个map任务处理。
5.7 hadoop自定义对象序列化
编写mapreduce 统计手机在一定时间内的上网流量
| 序号 |
字段 |
字段类型 |
描述信息 |
| 0 |
reportTime |
long |
记录报告时间戳 |
| 1 |
msisdn |
String |
手机号码 |
| 2 |
apmac |
String |
Ap mac 手机地址 |
| 3 |
acmac |
String |
Ac mac 运营商ip |
| 4 |
host |
String |
访问的网址 |
| 5 |
siteType |
String |
网站种类 |
| 6 |
upPackNum |
long |
上行数据包,单位:个 |
| 7 |
downPackNum |
long |
下行数据包,单位:个 |
| 8 |
upPayLoad |
long |
上行总流量。要注意单位的转换,单位,byte |
| 9 |
downPayLoad |
long |
下行总流量。要注意单位的转换,单位,byte |
| 10 |
httpStatus |
String |
HTTP Response的状态 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apathe.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apathe.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-core</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
| package com.dc;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class DataCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(DataCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(DCMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(DCReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class DCMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, DataBean>{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String files[] = line.split("/t");
String telNo = files[1];
Long up = Long.parseLong(files[8]);
Long down = Long.parseLong(files[9]);
DataBean db = new DataBean(telNo, up, down);
context.write(new Text(telNo), db);
}
}
public static class DCReducer extends Reducer<Text, DataBean, Text, DataBean>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<DataBean> v2s,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long up_sum = 0;
long down_sum = 0;
for(DataBean bean:v2s){
up_sum += bean.getUpPayLoad();
up_sum += bean.getDownPayLoad();
}
DataBean db = new DataBean("", up_sum, down_sum);
context.write(key, db);
}
}
}
package com.dc;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
public class DataBean implements Writable {
private String telNo;
private long upPayLoad;
private long downPayLoad;
private long totalPayLoad;
public DataBean(String telNo, long upPayLoad, long downPayLoad) {
super();
this.telNo = telNo;
this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad;
this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad;
this.totalPayLoad = upPayLoad+downPayLoad;
}
public DataBean() {
}
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(telNo);
out.writeLong(upPayLoad);
out.writeLong(downPayLoad);
out.writeLong(totalPayLoad);
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.telNo = in.readUTF();
this.upPayLoad = in.readLong();
this.downPayLoad = in.readLong();
this.totalPayLoad = in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.upPayLoad+"/"+this.downPayLoad+"/"+this.totalPayLoad;
};
public String getTelNo() {
return telNo;
}
public void setTelNo(String telNo) {
this.telNo = telNo;
}
public long getUpPayLoad() {
return upPayLoad;
}
public void setUpPayLoad(long upPayLoad) {
this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad;
}
public long getDownPayLoad() {
return downPayLoad;
}
public void setDownPayLoad(long downPayLoad) {
this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad;
}
public long getTotalPayLoad() {
return totalPayLoad;
}
public void setTotalPayLoad(long totalPayLoad) {
this.totalPayLoad = totalPayLoad;
}
}
|
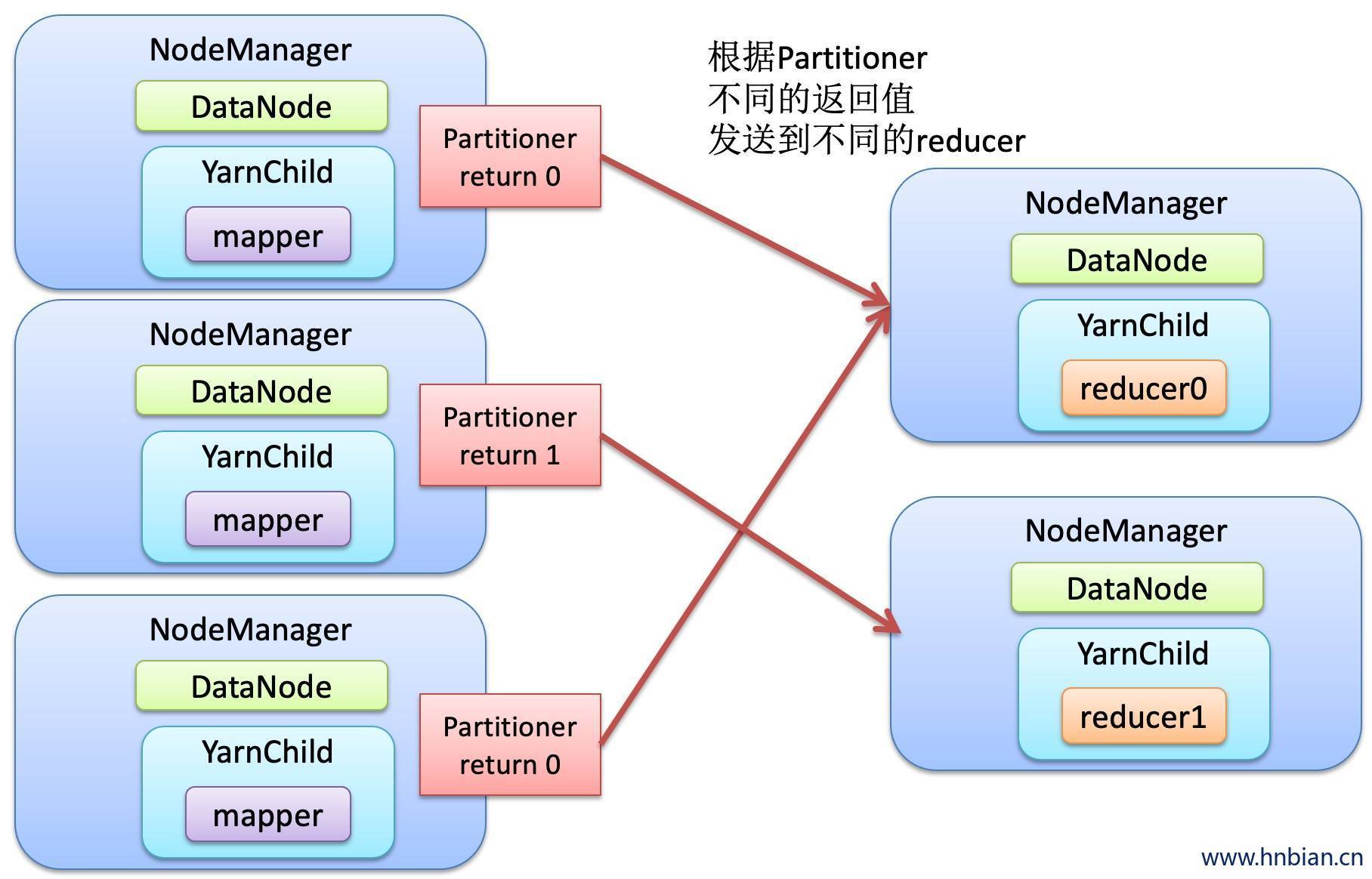
6. Partitioner编程
- Partitioner是Partitioner的基类,如果需要指定Partitioner也需要继承该类。
- HashPartitioner是MapReduce的默认Partitioner,计算方法是
Which reduce =(key.hashCode()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)%numReduceTasks,得到房前的目的reduce。
- 例子以jar形式运行(代码将手机号码按照指定运营商写到不同的reduce)其中databean同上
当设置的reducer数量 小于指定的reducer数量的时候会报错
当设置的reducer数量 大雨指定的reducer数量的时候不报错,但是后面几个结果为空
Map task 的并发数量是由切片的数量决定的,有多少个切片,就启动多少个map task,切片是一个逻辑概念,指的是文件中的偏移量范围,切片的具体大小应该根据所处理的文件大小调整的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
| package com.dc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class DataCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(DataCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(DCMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(DCReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setPartitionerClass(ProviderPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(Integer.parseInt(args[2]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class DCMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, DataBean>{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String files[] = line.split("/t");
String telNo = files[1];
Long up = Long.parseLong(files[8]);
Long down = Long.parseLong(files[9]);
DataBean db = new DataBean(telNo, up, down);
context.write(new Text(telNo), db);
}
}
public static class DCReducer extends Reducer<Text, DataBean, Text, DataBean>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<DataBean> v2s,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long up_sum = 0;
long down_sum = 0;
for(DataBean bean:v2s){
up_sum += bean.getUpPayLoad();
up_sum += bean.getDownPayLoad();
}
DataBean db = new DataBean("", up_sum, down_sum);
context.write(key, db);
}
}
public static class ProviderPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, DataBean>{
private static Map<String,Integer> providerMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
static{
providerMap.put("135", 1);
providerMap.put("138", 1);
providerMap.put("150", 2);
providerMap.put("159", 2);
providerMap.put("182", 3);
providerMap.put("183", 3);
}
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, DataBean value, int arg2) {
String account = key.toString();
String sub_acc = account.substring(0, 3);
Integer code = providerMap.get(sub_acc);
if(code==null){
code = 0;
}
return code;
}
}
}
|
对商家收入支出排序 按照收入高的排在前面 收入相同 按支出少的在前
将要排序的对象作为k2即可排序
如果是long 按照自然数
如果是text按照字典顺序
如果是bean按照自定义顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
|
package com.data;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class SumStep {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration con = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(con);
job.setJarByClass(SumStep.class);
job.setMapperClass(SumMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class SumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, InfoBean>{
private Text k = new Text();
private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String files[] = line.split("\t");
String account = files[0];
double in = Double.parseDouble(files[1]);
double out = Double.parseDouble(files[2]);
k.set(account);
v.set(account, in, out);
context.write(k, v);
}
}
public static class SumReducer extends Reducer<Text, InfoBean, Text, InfoBean>{
private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<InfoBean> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
double in_sum = 0;
double out_sum = 0;
for(InfoBean bean:values){
in_sum +=bean.getIncome();
out_sum +=bean.getExpenses();
}
v.set("", in_sum, out_sum);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
}
package com.data;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class SortStep {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration con = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(con);
job.setJarByClass(SortStep.class);
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(InfoBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,InfoBean, NullWritable>{
private InfoBean k = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String files[] = line.split("\t");
String account = files[0];
double in = Double.parseDouble(files[1]);
double out = Double.parseDouble(files[2]);
k.set(account, in, out);
context.write(k, NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class SortReducer extends Reducer<InfoBean, NullWritable, Text, InfoBean>{
private Text k = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(InfoBean bean, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String accten = bean.getAccount();
k.set(accten);
context.write(k, bean);
}
}
}
package com.data;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class InfoBean implements WritableComparable<InfoBean> {
private String account;
private double income;
private double expenses;
private double surplus;
public void set(String account,double income,double expenses){
this.account = account;
this.income = income;
this.expenses = expenses;
this.surplus = income - expenses;
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.account = in.readUTF();
this.income = in.readDouble();
this.expenses = in.readDouble();
this.surplus = in.readDouble();
}
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(account);
out.writeDouble(income);
out.writeDouble(expenses);
out.writeDouble(surplus);
}
public int compareTo(InfoBean ib) {
if(this.income == ib.getIncome()){
return this.expenses > ib.getExpenses() ? 1 : -1;
}else{
return this.income>ib.getIncome() ? -1 : 1;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.income+"\t"+this.expenses+"\t"+this.surplus;
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public double getIncome() {
return income;
}
public void setIncome(double income) {
this.income = income;
}
public double getExpenses() {
return expenses;
}
public void setExpenses(double expenses) {
this.expenses = expenses;
}
public double getSurplus() {
return surplus;
}
public void setSurplus(double surplus) {
this.surplus = surplus;
}
}
|
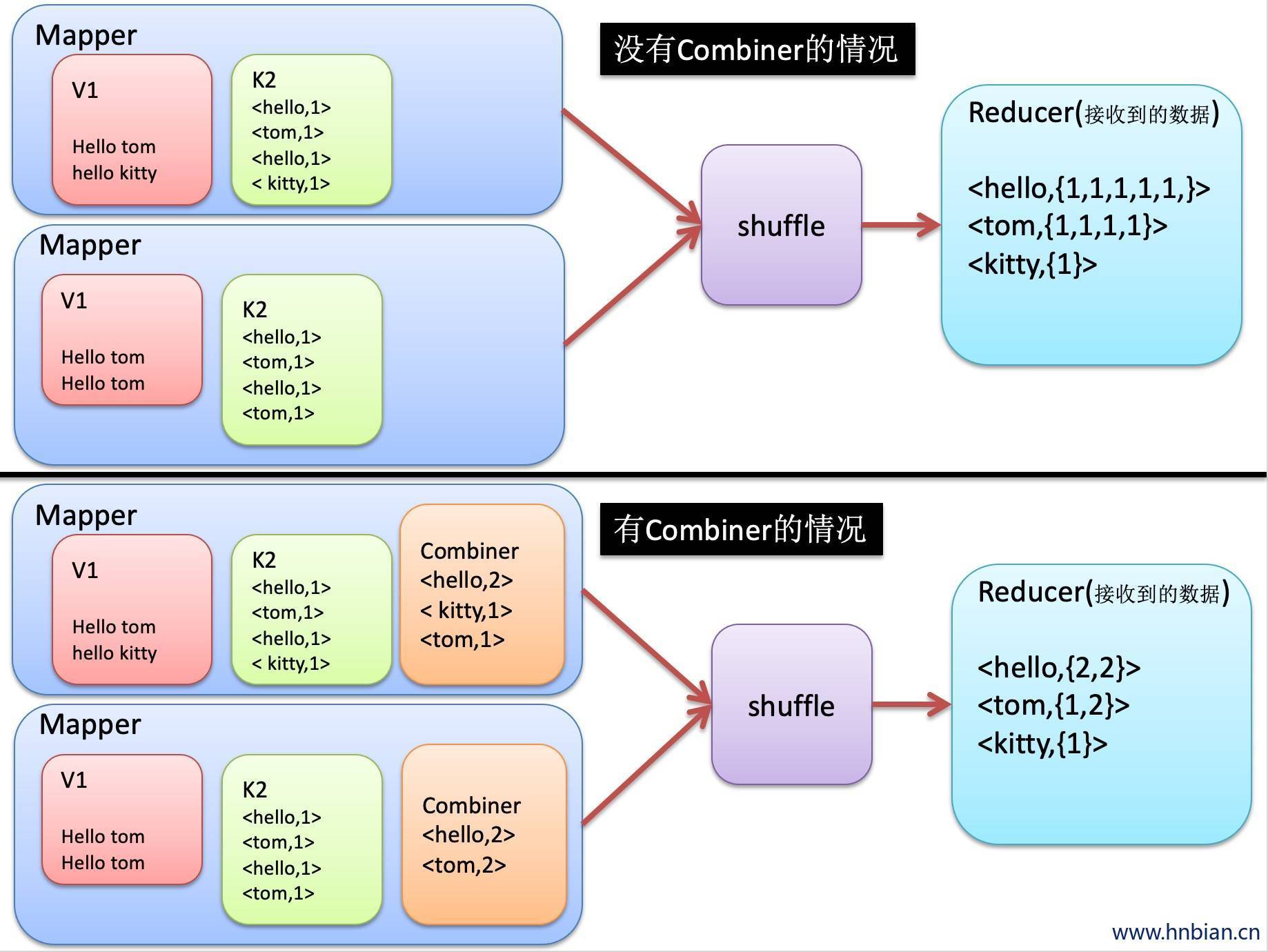
7. Combiners编程
- 每一个map可能会产生大量的输出,combiner的作用就是在map端对输出先做一次合并,减少输出到reduce的数据量
- combiners最基本是实现本地key的递归,combiner具有类似本地的reduce功能。
- 如果不用combiner,那么,所有的结果都是reduce完成,效率会相对低下,使用Combiner,先完成的map会在本地聚合,提升速度。
- 注意:Combiner的输出是Reduce的输入,结果Combiner是可插拔的,添加Combiner绝不能该不变最终的计算结果,所以Combiner只应该用于那种Reduce的输入key/value与输出key/value类型完全一致,且不影响最终结果的场景,比如累加、最大值等。
- map的输出是Combiner的输入,Combiner的输出是Reduce的输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
| package mr;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(WcMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/words.txt"));
job.setReducerClass(WcReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/wcOunt"));
job.setCombinerClass(WcReducer.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class WcReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text k2, Iterable<LongWritable> v2s,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Text k3 = k2;
long conter = 0;
for(LongWritable i:v2s){
conter +=i.get();
}
context.write(k3,new LongWritable(conter));
}
}
public static class WcMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String words[] = line.split(" ");
for(String w:words){
context.write(new Text(w), new LongWritable(1));
}
}
}
}
|
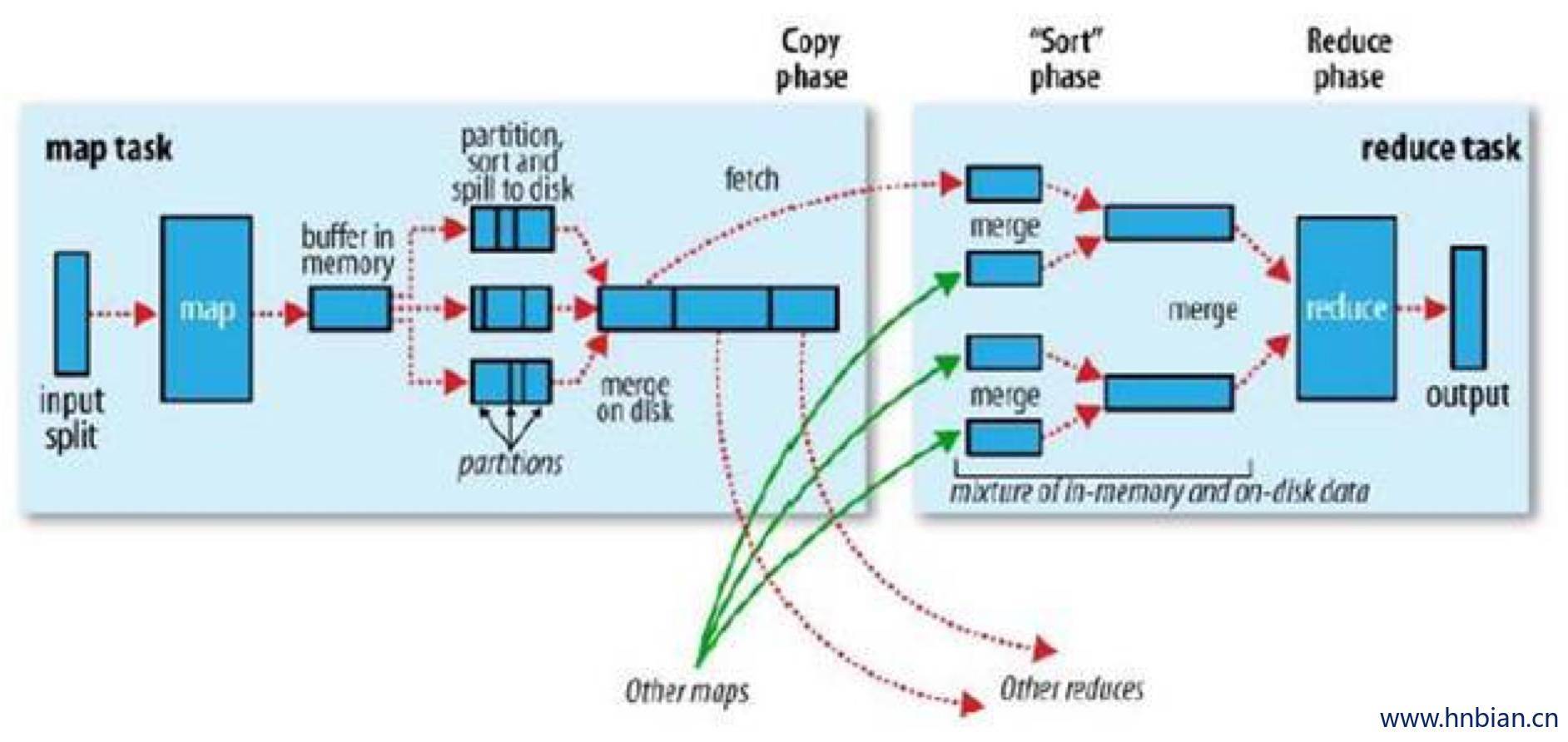
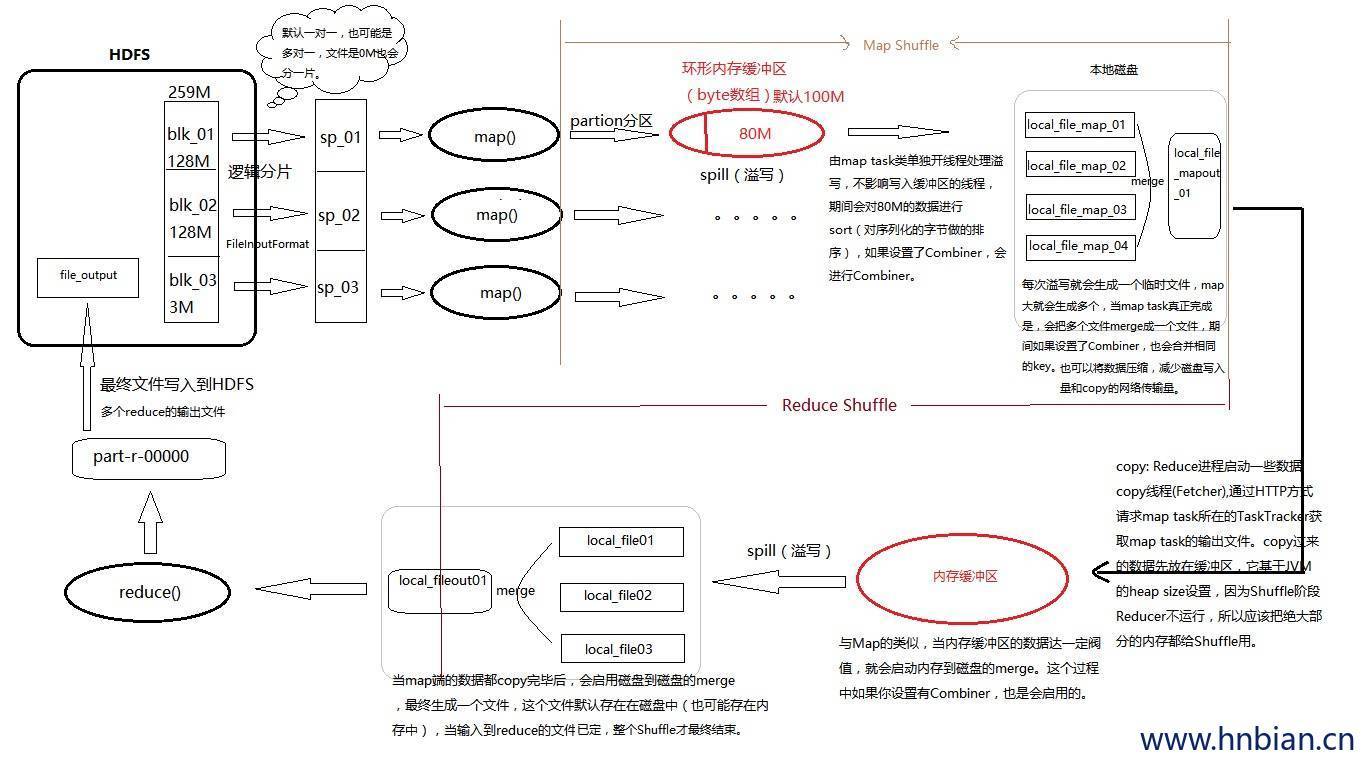
8. Shuffle
一个输入切片对应一个mapper,
一个mapper读取文件的一部分,每一个mapper都有一个环形缓冲区(环形缓冲区在内存中)
环形缓冲区用来存储map的输出,如果内存中的数据满了(默认100M),
当map向内存中写的数据达到一定阀值(80%),后台进程便将数据溢写到磁盘,
-
mapper向环形缓冲区速度快,内存向磁盘写数据慢,当内存写满之后Mapper堵塞,直到内存中的数据写入到小文件全部写完,内存写到下一个小文件。
会产生很多分区且排序的小文件
小文件还会合并成大文件
相同分区号的文件进行合并(0号分区的数据与0号分区的数据进行合并。。。)合并之后再进行一次排序,得到分区切排序的大文件
mapper的任务完成了
接下来到reducer
reducer获取mapper的数据
reducer启动之初就对其进行编号,在获取数据的时候按照(0号reducer取0号分区里面的数据。。。)来进行
8.1 Shuffer 代码示例(倒排索引)
倒排索引过程
Map阶段
<0,”hello tom”>
….
context.write(“hello->a.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->a.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->a.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->a.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->a.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->b.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->b.txt”,1);
context.write(“hello->b.txt”,1);
-——————————————————-
combiner阶段
<”hello->a.txt”,1>
<”hello->a.txt”,1>
<”hello->a.txt”,1>
<”hello->a.txt”,1>
<”hello->a.txt”,1>
<”hello->b.txt”,1>
<”hello->b.txt”,1>
<”hello->b.txt”,1>
context.write(“hello”,”a.txt->5”);
context.write(“hello”,”b.txt->3”);
-——————————————————-
Reducer阶段
<”hello”,{“a.txt->5”,”b.txt->3”}>
context.write(“hello”,”a.txt->5 b.txt->3”);
-——————————————————
hello “a.txt->5 b.txt->3”
tom “a.txt->2 b.txt->1”
kitty “a.txt->1”
…….
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| package com.ii;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class InverseIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration con = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(con);
job.setJarByClass(InverseIndex.class);
job.setMapperClass(IndexMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setCombinerClass(IndexCombinner.class);
job.setReducerClass(IndexReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class IndexMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{
private Text k = new Text();
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String words[] = line.split(" ");
FileSplit is = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
String path = is.getPath().toString();
for(String w:words){
k.set(w+"->"+path);
v.set("1");;
context.write(k, v);
}
}
}
public static class IndexCombinner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
private Text k = new Text();
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String wordAndPath [] = key.toString().split("->");
String word = wordAndPath[0];
String path = wordAndPath[1];
int counter = 0;
for(Text t:values){
counter += Integer.parseInt(t.toString());
}
k.set(word);
v.set(path+"->"+counter);
context.write(k,v);
}
}
public static class IndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String result = "";
for(Text t:values){
result +=t.toString()+"\t";
}
v.set(result);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
}
|











