1. 多层感知机
1.1 算法介绍
多层感知器 (MLP, Multilayer Perceptron) 是一种多层的前馈神经网络模型,所谓前馈型神经网络,指其从输入层开始只接收前一层的输入,并把计算结果输出到后一层,并不会给前一层有所反馈,整个过程可以使用有向无环图来表示。该类型的神经网络由三层组成,分别是输入层 (Input Layer),一个或多个隐层 (Hidden Layer),输出层 (Output Layer),如图所示:
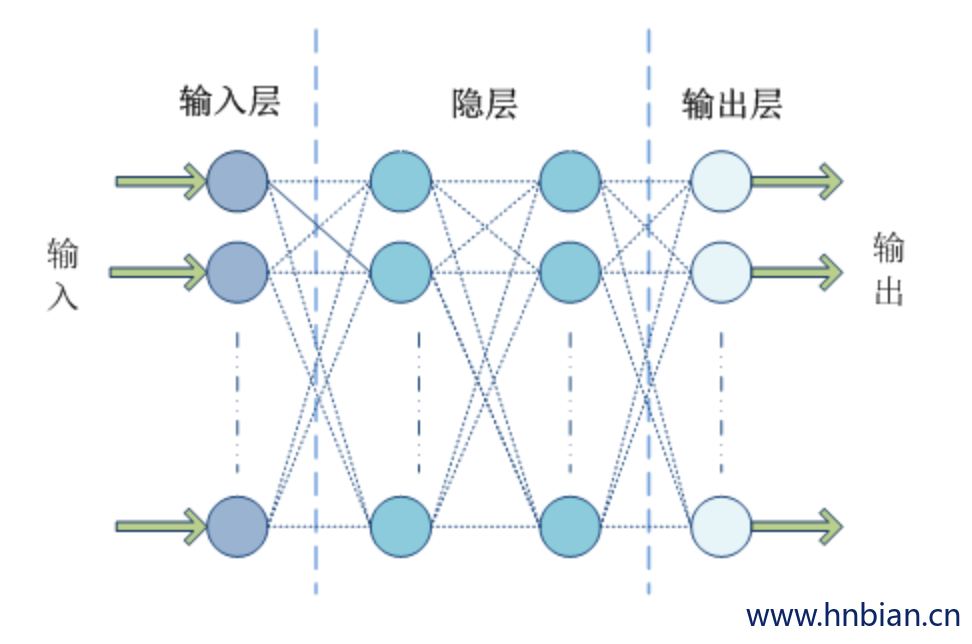
Spark ML 在 1.5 版本后提供一个使用 BP(反向传播,Back Propagation) 算法训练的多层感知器实现,BP 算法的学习目的是对网络的连接权值进行调整,使得调整后的网络对任一输入都能得到所期望的输出。BP 算法名称里的反向传播指的是该算法在训练网络的过程中逐层反向传递误差,逐一修改神经元间的连接权值,以使网络对输入信息经过计算后所得到的输出能达到期望的误差。Spark 的多层感知器隐层神经元使用 sigmoid 函数作为激活函数,输出层使用的是 softmax 函数。
模型中间层节点使用 sigmoid 方程:$y(Z_i) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-z} i}$
输出层使用 softmax 方程:$y(z_i) = \frac{e^zi}{\sum_{k=1}^n e^z k}$
输出层中 N 代表类别数目
1.2 参数说明
| 参数名称 |
类型 |
说明 |
| featuresCol |
字符串 |
特征列名 |
| labelCol |
字符串 |
标签列名 |
| predictionCol |
字符串 |
预测结果列名 |
| layers |
整数数组 |
这个参数是一个整型数组类型,
第一个元素需要和特征向量的维度相等,
最后一个元素需要训练数据的标签取值个数相等,如 2 分类问题就写 2。
中间的元素有多少个就代表神经网络有多少个隐层,
元素的取值代表了该层的神经元的个数。
例如
Scala1234
// 100个维度
// 两个隐层,第一个隐层6个神经元,第二个隐层5个神经元
// 2分类val layers = ArrayInt |
| maxIter |
整数 |
优化算法求解的最大迭代次数(>=0)。默认值是 100。 |
| seed |
长整型 |
随机种子 |
| stepSize |
双精度型 |
每次迭代优化步长该参数被前馈网络训练器
用来将训练样本数据的每个分区都按照 blockSize 大小分成不同组,
并且每个组内的每个样本都会被叠加成一个向量,以便于在各种优化算法间传递。
该参数的推荐值是 10-1000,默认值是 128。 |
| tol |
双精度 |
优化算法迭代求解过程的收敛阀值。默认值是 1e-4。不能为负数。 |
1.3 train方法源码简单解读
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
override protected def train(
dataset: Dataset[_]): MultilayerPerceptronClassificationModel = instrumented { instr =>
instr.logPipelineStage(this)
instr.logDataset(dataset)
instr.logParams(this, labelCol, featuresCol, predictionCol, layers, maxIter, tol,
blockSize, solver, stepSize, seed)
val myLayers = $(layers)
val labels = myLayers.last
instr.logNumClasses(labels)
instr.logNumFeatures(myLayers.head)
val encodedLabelCol = "_encoded" + $(labelCol)
val encodeModel = new OneHotEncoderModel(uid, Array(labels))
.setInputCols(Array($(labelCol)))
.setOutputCols(Array(encodedLabelCol))
.setDropLast(false)
val encodedDataset = encodeModel.transform(dataset)
val data = encodedDataset.select($(featuresCol), encodedLabelCol).rdd.map {
case Row(features: Vector, encodedLabel: Vector) => (features, encodedLabel)
}
val topology = FeedForwardTopology.multiLayerPerceptron(myLayers, softmaxOnTop = true)
val trainer = new FeedForwardTrainer(topology, myLayers(0), myLayers.last)
if (isDefined(initialWeights)) {
trainer.setWeights($(initialWeights))
} else {
trainer.setSeed($(seed))
}
if ($(solver) == MultilayerPerceptronClassifier.LBFGS) {
trainer.LBFGSOptimizer
.setConvergenceTol($(tol))
.setNumIterations($(maxIter))
} else if ($(solver) == MultilayerPerceptronClassifier.GD) {
trainer.SGDOptimizer
.setNumIterations($(maxIter))
.setConvergenceTol($(tol))
.setStepSize($(stepSize))
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
s"The solver $solver is not supported by MultilayerPerceptronClassifier.")
}
trainer.setStackSize($(blockSize))
val mlpModel = trainer.train(data)
new MultilayerPerceptronClassificationModel(uid, myLayers, mlpModel.weights)
}
|
1.4 代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| package hnbian.sparkml.algorithms.classification
import hnbian.spark.utils.SparkUtils
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
import utils.FileUtils
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.MultilayerPerceptronClassifier
object MultilayerPerceptronClassifier extends App {
val spark = SparkUtils.getSparkSession("MultilayerPerceptronClassifier", 4)
val filePath = FileUtils.getFilePath("sample_multiclass_classification_data.txt")
val data = spark.read.format("libsvm").load(filePath)
data.show()
val Array(train, test) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 1234L)
val layers = Array[Int](4, 5, 4, 3)
val trainer = new MultilayerPerceptronClassifier()
.setLayers(layers)
.setBlockSize(128)
.setSeed(1234L)
.setMaxIter(100)
val model = trainer.fit(train)
val predictions = model.transform(test)
predictions.show(3)
val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(
predictions.select("prediction", "label")
.rdd.map {
case Row(prediction: Double, label: Double) => (prediction, label)
}
)
println("\n\n========= 评估结果 ==========")
println(s"\n准确率:$metrics.accuracy")
println(s"加权精确率:$metrics.weightedPrecision")
println(s"加权召回率:$metrics.weightedRecall")
println(s"F1值:$metrics.weightedFMeasure")
}
|
2. 一对多分类器
2.1 算法介绍
OneVsRest 将一个给定的二分类算法有效地扩展到多分类问题应用中, 也叫做 “ One-vs-All” 算法。 OneVsRest 是一个 Estimator。 它采用一个基础的Classfier 然后对于K个类别分别创建二分类问题。 类别 i 的二分类分类器用来预测类别为 i 还是不为 i , 即将 i 类和其他类别区分开来。 最后。 通过一次对K个二分类分类器进行评估, 取置信最高的分类器的标签作为 i 类别的标签。
2.2 参数说明
| 参数名称 |
类型 |
说明 |
| featuresCol |
字符串 |
特征列名 |
| labelCol |
字符串 |
标签列名 |
| predictionCol |
字符串 |
预测结果列名 |
| classifier |
分类器 |
基础二分类分类器 |
2.3 代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| package hnbian.sparkml.algorithms.classification
import hnbian.spark.utils.SparkUtils
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
import utils.FileUtils
object OneVsRest extends App {
val spark = SparkUtils.getSparkSession("OneVsRest", 4)
val filePath = FileUtils.getFilePath("sample_libsvm_data.txt")
val inputData = spark.read.format("libsvm").load(filePath)
inputData.show(3)
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.{LogisticRegression, OneVsRest}
val Array(train, test) = inputData.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2))
val classifier = new LogisticRegression()
.setMaxIter(10)
.setTol(1E-6)
.setFitIntercept(true)
val ovr = new OneVsRest().setClassifier(classifier)
val ovrModel = ovr.fit(train)
val predictions = ovrModel.transform(test)
predictions.show(2)
val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(
predictions.select("prediction", "label")
.rdd.map {
case Row(prediction: Double, label: Double) => (prediction, label)
}
)
println("\n\n========= 评估结果 ==========")
println(s"\n准确率:${metrics.accuracy}")
println(s"加权精确率:${metrics.weightedPrecision}")
println(s"加权召回率:${metrics.weightedRecall}")
println(s"F1值:${metrics.weightedFMeasure}")
}
|
3. 朴素贝叶斯
在机器学习中,朴素贝叶斯分类器是一系列以假设特征之间强(朴素)独立下运用贝叶斯定理为基础的简单概率分类器
——维基百科
算法类型: 分类算法
3.1 算法介绍
朴素贝叶斯算法是基于贝叶斯定理与特征独立假设的分类算法。
朴素贝叶斯的思想基础是这样的:对于给出的待分类项, 求解在此项出现的条件下各个类别的出现概率, 在没有其他可用信息下, 我们会选在条件概率最大的类别作为此待分类项应属的类别。
3.2 公式解析
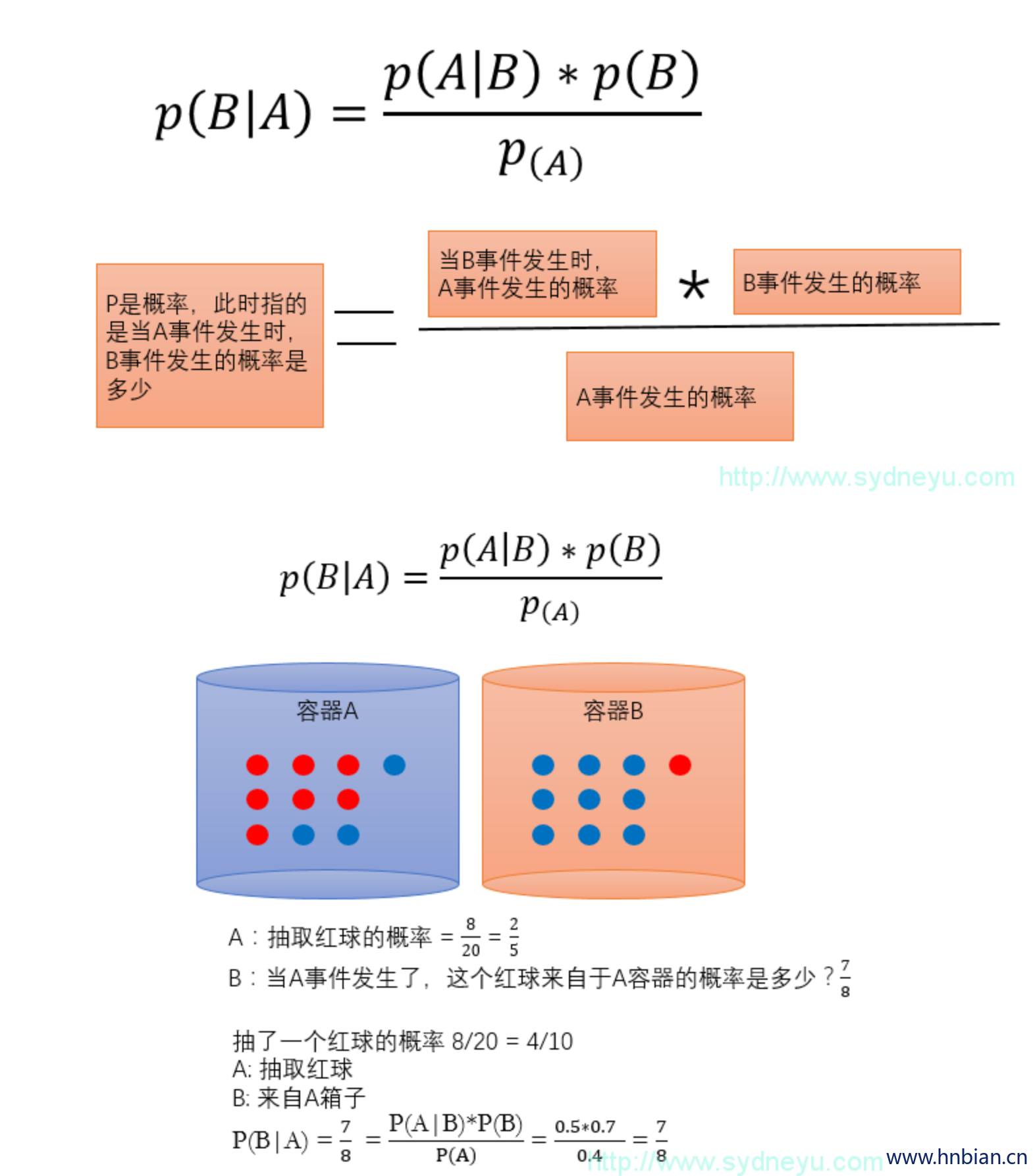
3.3 参数说明
| 参数名称 |
类型 |
说明 |
| featuresCol |
字符串 |
特征列名 |
| labelCol |
字符串 |
标签列名 |
| predictionCol |
字符串 |
预测结果列名 |
| probabilityCol |
字符串 |
用以预测类别条件概率的列名 |
| rawPredictionCol |
字符串 |
原始预测 |
| modelType |
字符串 |
模型类型(区分大小写) |
| smoothing |
双精度 |
平滑参数 |
| thresholds |
双精度数组 |
多分类预测的阀值,以调整预测结果在各个类别的概率 |
3.4 代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| package hnbian.sparkml.algorithms.classification
import hnbian.spark.utils.SparkUtils
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
import utils.FileUtils
object NaiveBayes extends App {
val spark = SparkUtils.getSparkSession("NaiveBayes", 4)
val filePath = FileUtils.getFilePath("sample_libsvm_data.txt")
val data = spark.read.format("libsvm").load(filePath)
data.show()
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.NaiveBayes
import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator
val Array(trainingData, testData) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3), seed = 1234L)
val model = new NaiveBayes()
.fit(trainingData)
val predictions = model.transform(testData)
predictions.show()
val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(
predictions.select("prediction", "label")
.rdd.map {
case Row(prediction: Double, label: Double) => (prediction, label)
}
)
println("\n\n评估结果")
println(s"\n准确率:${metrics.accuracy}")
println(s"加权精确率:${metrics.weightedPrecision}")
println(s"加权召回率:${metrics.weightedRecall}")
println(s"F1值:${metrics.weightedFMeasure}")
}
|
4. 支持向量机
4.1 方法简介
支持向量机SVM(support vector machine)是一种二分类模型。它的基本模型是定义在特征空间上的间隔最大的线性分类器。支持向量机学习方法包含3种模型:线性可分支持向量机、线性支持向量机及非线性支持向量机。
- 当训练数据线性可分时,通过硬间隔最大化,学习一个线性的分类器,即线性可分支持向量机;
- 当训练数据近似线性可分时,通过软间隔最大化,也学习一个线性的分类器,即线性支持向量机;
- 当训练数据线性不可分时,通过使用核技巧及软间隔最大化,学习非线性支持向量机。
线性支持向量机支持L1和L2的正则化变型。关于正则化,可以参见http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.6.2/mllib-linear-methods.html#regularizers
4.2 基本原理
SVM从线性可分情况下的最优分类面发展而来。最优分类面就是要求分类线不但能将两类正确分开(训练错误率为0),且使分类间隔最大。SVM考虑寻找一个满足分类要求的超平面,并且使训练集中的点距离分类面尽可能的远,也就是寻找一个分类面使它两侧的空白区域(margin)最大。这两类样本中离分类面最近,且平行于最优分类面的超平面上的点,就叫做支持向量(下图中红色的点)。
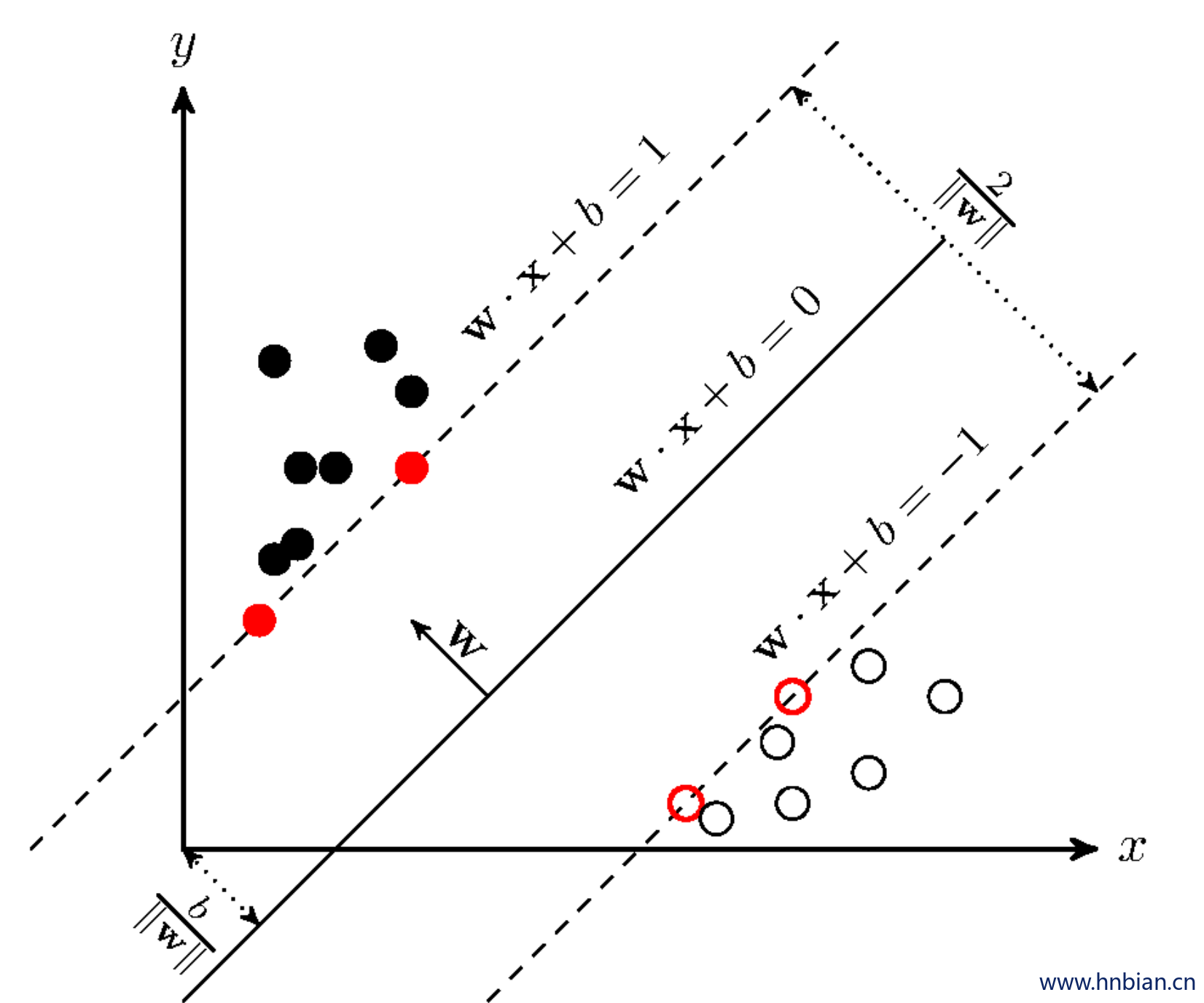
4.3 参数说明
| RegParam |
设置正则化参数。默认 0.0. |
| MaxIter |
设置最大迭代次数默认 100. |
| FitIntercept |
Whether to fit an intercept term.默认 true. |
| Tol |
设置迭代的收敛容差。 较小的值将导致更高的准确性,代价是更多的迭代。默认 1E-6. |
| Standardization |
是否在拟合模型之前标准化训练特征。默认 true. |
| WeightCol |
设置param [[weightCol]]的值。如果未设置或为空,则将所有实例权重视为1.0。默认值未设置,因此所有实例都具有权重1。 |
| Threshold |
二分类预测的阈值, 范围[0,1] |
| AggregationDepth |
treeAggregate的建议深度(大于或等于2)。如果特征或分区的数量很大,这个参数可以调整到更大的尺寸。默认 2. |
4.4 示例代码
下面的例子具体介绍了如何读入一个数据集,然后用SVM对训练数据进行训练,然后用训练得到的模型对测试集进行预测,并计算错误率。以iris数据集(https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data)为例进行分析。iris以鸢尾花的特征作为数据来源,数据集包含150个数据集,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性,是在数据挖掘、数据分类中非常常用的测试集、训练集。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| package hnbian.sparkml.algorithms.classification
import hnbian.spark.utils.SparkUtils
import hnbian.sparkml.utils.Evaluations
import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.StringIndexer
import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.LinearSVC
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
import utils.FileUtils
object SVM extends App {
val spark = SparkUtils.getSparkSession("SVM", 4)
val filePath = FileUtils.getFilePath("iris.txt")
import spark.implicits._
val data = spark.sparkContext
.textFile(filePath)
.map(_.split(","))
.map(p => Iris(Vectors.dense(p(0).toDouble, p(1).toDouble, p(2).toDouble, p(3).toDouble), p(4).toString()))
.filter(p=>{p.labelCol !="Iris-versicolor"})
.toDF()
data.show()
val labelIndexer = new StringIndexer()
.setInputCol("labelCol")
.setOutputCol("label")
.fit(data)
val labelIndexerData = labelIndexer.transform(data)
labelIndexerData.persist()
labelIndexerData.show(30)
val Array(trainingData, testData) = labelIndexerData.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
val lsvc = new LinearSVC().setRegParam(0.3).setMaxIter(100)
val model = lsvc.fit(trainingData)
val predictions = model.transform(testData)
predictions.show()
labelIndexerData.unpersist()
val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(
predictions.select("prediction", "label")
.rdd.map {
case Row(prediction: Double, label: Double) => (prediction, label)
}
)
println("\n\n评估结果")
println(s"\n准确率:${metrics.accuracy}")
println(s"加权精确率:${metrics.weightedPrecision}")
println(s"加权召回率:${metrics.weightedRecall}")
println(s"F1值:${metrics.weightedFMeasure}")
}
case class Iris(features: org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vector, labelCol: String)
|




