1. 介绍
clickhouse 对 SQL 语句的解析时大小写敏感的,这就意味这,select a 和 select A 表达的语义是不同的
clickhouse 支持的查询语法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 [with expr | ( subquery ) ] select [ distinct ] expr[ from [ db. ]table | ( subquery ) | table_function ] [ final ] [ sample expr ] [ [ left ] array join ] [ global ] [ all | any | asof ] [ inner | cross | [ left | right | full [ outer ] ] ] join ( subquery ) | table on | using columns_list [ prewhere expr ] [ where expr ] [ group by expr ] [ with rollup | cube | totals ] [ having expr ] [ order by expr ] [ limit [ n [ ,m ] ] ] [ union all ] [ into outfile finename ] [ format format ] [ limit [ offset ] n by columns ] / / 方括号内的查询子句为可选项,所以只有 select 子句是必须的/ / clickhouse 对查询语法的解析大致也是按照上面各个子句排列的顺序进行的/ / 下面介绍查询语法时也会按照上面的顺序进行介绍
2. with 子句 2.1 介绍 clickhouse 支持 公共表表达式 (CTE, Common Table Expressions)以增强查询语句的表达,如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 select pow(pow(2 ,2 ),3 ) as result ;┌─result ─┐ │ 64 │ └────────┘ WITH pow(2 , 2 ) AS aSELECT pow(a, 3 ) AS result ;┌─result ─┐ │ 64 │ └────────┘
CTE 通过 with 子句表示,还支持下面几种用法
2.2 定义变量 可以定义变量,这些变量在后面查询中能够直接被访问。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 WITH 5 AS end SELECT number FROM system.numbersWHERE number < 5 LIMIT 3 ; ┌─number─┐ │ 0 │ │ 1 │ │ 2 │ └────────
2.3 调用函数 可以访问 select 子句中的列字段,并调用函数做进一步的处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 SELECT database, formatReadableSize(sum (data_uncompressed_bytes) ) AS format FROM system.columnsGROUP BY databaseORDER BY format DESC ;┌─database──────────┬─format────┐ │ system │ 1.92 GiB │ │ db1 │ 0.00 B │ │ db2 │ 0.00 B │ │ db_merge │ 0.00 B │ │ default │ 0.00 B │ │ db_Dictionary │ 0.00 B │ │ test_dictionaries │ 0.00 B │ └───────────────────┴───────────┘ WITH sum (data_uncompressed_bytes) AS bytesSELECT database, formatReadableSize(bytes) AS format FROM system.columnsGROUP BY databaseORDER BY bytes DESC ;┌─database──────────┬─format────┐ │ system │ 1.92 GiB │ │ db1 │ 0.00 B │ │ db2 │ 0.00 B │ │ db_merge │ 0.00 B │ │ default │ 0.00 B │ │ db_Dictionary │ 0.00 B │ │ test_dictionaries │ 0.00 B │ └───────────────────┴───────────┘
2.4 定义子查询 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 WITH ( SELECT count (1 ) FROM system.columns ) AS total_columns SELECT table , count (table ) AS columns_count, (count (table ) / total_columns) * 100 AS column_rate FROM system.columnsGROUP BY table ORDER BY column_rate DESC LIMIT 3 ; ┌─table ──────┬─columns_count─┬────────column_rate─┐ │ metric_log │ 272 │ 21.829855537720707 │ │ query_log │ 62 │ 4.975922953451043 │ │ parts │ 51 │ 4.093097913322633 │ └────────────┴───────────────┴────────────────────┘
2.5 在子查询中重复使用 with 可以在子查询中嵌套使用 with 子句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 with ( round(column_rate) ) as column_rate_v1 select table , columns_count, column_rate, column_rate_v1 from ( WITH ( SELECT count (1 ) FROM system.columns ) AS total_columns SELECT table , count (table ) AS columns_count, (count (table ) / total_columns) * 100 AS column_rate FROM system.columns GROUP BY table ORDER BY column_rate DESC LIMIT 3 ); ┌─table ──────┬─columns_count─┬────────column_rate─┬─column_rate_v1─┐ │ metric_log │ 272 │ 21.829855537720707 │ 22 │ │ query_log │ 62 │ 4.975922953451043 │ 5 │ │ parts │ 51 │ 4.093097913322633 │ 4 │ └────────────┴───────────────┴────────────────────┴────────────────┘
3. from 子句 from 子句表示从何处读数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 select name from system.columns limit 3 ;┌─name───────────┐ │ department_id │ │ employee_count │ │ salary_count │ └────────────────┘ select name from ( select name from system.columns limit 3 ) ; ┌─name───────────┐ │ department_id │ │ employee_count │ │ salary_count │ └────────────────┘ select number from numbers(3 );┌─number─┐ │ 0 │ │ 1 │ │ 2 │ └────────┘
from 关键字合一省略,此时会从续表中取数据,在 clickhouse 中并没有数据库中常见的 dual 虚表,而是用 system.one
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 select 1 ;┌─1 ─┐ │ 1 │ └───┘ select 1 from system.one;┌─1 ─┐ │ 1 │ └───┘
from 子句后面可以使用 final 修饰符。它可以配合 collapsingMergeTree 和 Versioned-CollapsingMergeTree 等表引擎进行查询操作,以强制查询过程中合并,但是由于 final 修饰符会降低查询性能,所以应该尽可能避免使用它。
4. sample 子句 4.1 介绍
Sample 子句能够实现数据采样的功能,查询仅返回采样数据而不是全部数据,从而减少查询负载。
Sample 子句的采样机制是一种幂等的设计,在数据不发声变化的情况下,相同的规则返回的数据时相同的。
Sample 子句适合在可以接收近似查询结果的场合下使用,例如数据量巨大,对查询的实效性要求大于准确性的情况。
Sample 子句只能用于 MergeTree 表达式,并且建表时需要声明 sample by 抽样表达式。
使用示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 create table t_sample( id UInt8, name String, date DateTime ) engine = MergeTree() partition by toYYYYMM(date )order by (id,intHash32(id))sample by intHash32(id); / / 写入数据insert into t_sample values (1 ,'小明' ,'2021-06-26 11:40:41' );insert into t_sample values (2 ,'小红' ,'2021-06-26 11:40:42' );insert into t_sample values (3 ,'小刚' ,'2021-06-26 11:40:43' );insert into t_sample values (4 ,'小东' ,'2021-06-26 11:40:44' );insert into t_sample values (5 ,'小丽' ,'2021-06-26 11:40:45' );
4.2 sample factor sample factor 表示按照因子系数采样,其中 factor 表示采样因子,它的取值支持 0-1 之间的小数,如果 factor 设置为 0 或者 1 则效果等同于不进行采样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 select id,name from t_sample sample 0.4 ;┌─id─┬─name─┐ │ 1 │ 小明 │ │ 3 │ 小刚 │ └────┴──────┘ select id,name from t_sample sample 40 / 100 ;
在进行统计查询时,为了得到最终的近似结果,需要将得到的直接结果乘以采样系数,若想要按 0.4 的因子采样,则需要将统计结果放大十倍。
1 2 3 4 select count (1 ) * 10 as sample from t_sample sample 0.4 ;┌─sample─┐ │ 20 │ └────────┘
还有一种方法是借助虚拟字段 _sample_factor 来获取采样稀疏,并以此代替硬编码的形式,_sample_factor 可以返回当前查询多对应的采样系数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 select id,_sample_factor from t_sample sample 0.4 ;┌─id─┬─_sample_factor─┐ │ 1 │ 2.5 │ │ 3 │ 2.5 │ └────┴────────────────┘ select count (1 ) * any (_sample_factor) from t_sample sample 0.4 ;┌─multiply(count (), any (_sample_factor))─┐ │ 5 │ └────────────────────────────────────────┘
4.3 sample rows
sample rows 是按照数量采样,其中 rows 表示至少采样多少行数据,它的取值必须是大于 1,如果 rows 的取值大于 表内的总行数,则效果等于1 即不采样。
sample rows 采样数量 的最小粒度是由 index_granularity 索引粒度决定的,所以设置一个小于索引粒度或者较小的值是没什么意义的,应该设置以为稍大的值。
sample rows 采样 同样可以使用 _sample_factor 来获取当前查询所对应的采样系数。
1 2 3 4 select id,_sample_factor from t_sample sample 10000 limit 1 ;┌─id─┬─_sample_factor─┐ │ 1 │ 1 │ └────┴────────────────┘
4.4 sample factor offset n sample factor offset n 表示按照因子系数和偏移量采样,其中 factor 表示采样因子,n 表示便宜多少数据后才进行 CIA杨,他们的取值都是 0-1 之间的小数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 select id,name from t_sample sample 0.4 offset 0.5 ;┌─id─┬─name─┐ │ 5 │ 小丽 │ └────┴──────┘
5. array join 子句 5.1 介绍
array join 子句允许在数据表的内部与数组或嵌套类型的字段进行 join 操作,从而进行一行数据组展开为多行。
在一条 select 语句中,不使用子查询的情况下,只能存在一个 array join 子句,
array join 子句支持 inner 和 left 两种策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 create table t_array_join( title String, value Array (UInt8) ) ENGINE= Log; insert into t_array_join values ('food' ,[1 ,2 ,3 ]), ('fruit' ,[3 ,4 ]), ('meat' ,[]); drop table t_array_join;
5.2 inner array join
array join 在默认情况下,使用的是 inner join 策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 select title,value from t_array_join array join value ;┌─title─┬─value ─┐ │ food │ 1 │ │ food │ 2 │ │ food │ 3 │ │ fruit │ 3 │ │ fruit │ 4 │ └───────┴───────┘ select title,value ,v from t_array_join array join value as v;┌─title─┬─value ───┬─v─┐ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 1 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 2 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 3 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 3 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 4 │ └───────┴─────────┴───┘
5.3 left array join 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 select title,value from t_array_join left array join value ;┌─title─┬─value ─┐ │ food │ 1 │ │ food │ 2 │ │ food │ 3 │ │ fruit │ 3 │ │ fruit │ 4 │ │ meat │ 0 │ └───────┴───────┘ select title,value ,v from t_array_join left array join value as v;┌─title─┬─value ───┬─v─┐ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 1 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 2 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 3 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 3 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 4 │ │ meat │ [] │ 0 │ └───────┴─────────┴───┘
当同时对多个数组字段进行 array join 操作时,查询的计算逻辑是按照行进行合并而不是产生笛卡尔积
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 SELECT title, value , v, arrayMap(x - > (x * 2 ), value ) AS mapv, v1 FROM t_array_joinLEFT ARRAY JOIN value AS v, mapv AS v1; ┌─title─┬─value ───┬─v─┬─mapv────┬─v1─┐ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 1 │ [2 ,4 ,6 ] │ 2 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 2 │ [2 ,4 ,6 ] │ 4 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 3 │ [2 ,4 ,6 ] │ 6 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 3 │ [6 ,8 ] │ 6 │ │ fruit │ [3 ,4 ] │ 4 │ [6 ,8 ] │ 8 │ │ meat │ [] │ 0 │ [] │ 0 │ └───────┴─────────┴───┴─────────┴────┘
在介绍数据类型时说过,嵌套类型的本质是数组,所以 arrau join 也支持嵌套类型的数据,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 create table t_array_join_nested( title String, nest Nested( v1 UInt32, v2 UInt64 ) ) ENGINE= Log; insert into t_array_join_nested values ('food' ,[1 ,2 ,3 ],[10 ,20 ,30 ]), ('fruit' ,[4 ,5 ],[40 ,50 ]), ('meat' ,[],[]); select title,nest.v1,nest.v2 from t_array_join_nested array join nest.v1,nest.v2;┌─title─┬─nest.v1─┬─nest.v2─┐ │ food │ 1 │ 10 │ │ food │ 2 │ 20 │ │ food │ 3 │ 30 │ │ fruit │ 4 │ 40 │ │ fruit │ 5 │ 50 │ └───────┴─────────┴─────────┘ select title,nest.v1,nest.v2 from t_array_join_nested array join nest.v1;┌─title─┬─nest.v1─┬─nest.v2────┐ │ food │ 1 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ │ food │ 2 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ │ food │ 3 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ │ fruit │ 4 │ [40 ,50 ] │ │ fruit │ 5 │ [40 ,50 ] │ └───────┴─────────┴────────────┘ select title,nest.v1,v1_1,nest.v2,v2_1 from t_array_join_nested array join nest.v1 as v1_1,nest.v2 as v2_1;┌─title─┬─nest.v1─┬─v1_1─┬─nest.v2────┬─v2_1─┐ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 1 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ 10 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 2 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ 20 │ │ food │ [1 ,2 ,3 ] │ 3 │ [10 ,20 ,30 ] │ 30 │ │ fruit │ [4 ,5 ] │ 4 │ [40 ,50 ] │ 40 │ │ fruit │ [4 ,5 ] │ 5 │ [40 ,50 ] │ 50 │ └───────┴─────────┴──────┴────────────┴──────┘
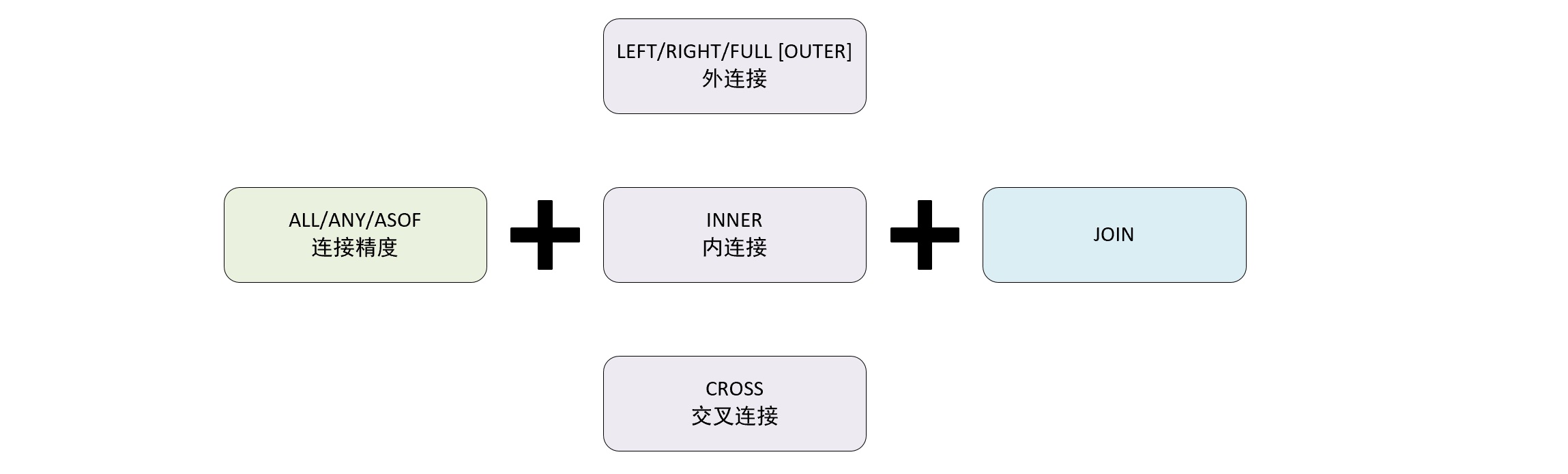
6. join 子句 6.1 介绍 join 子句 可以对左右两张表的数据进行连接,它的语法包含连接精度和连接类型两个部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 create table t_join1( id String, name String, time DateTime ) ENGINE= Log; insert into t_join1 values ('1' ,'clickhouse' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:01' ), ('2' ,'spark' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:02' ), ('3' ,'es' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:03' ), ('4' ,'hbase' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:04' ), ('' ,'clickhouse' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:05' ), ('' ,'spark' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:06' ); create table t_join2( id String, rate UInt8, time DateTime ) ENGINE= Log; insert into t_join2 values ('1' ,'100' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:01' ), ('1' ,'95' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:01' ), ('2' ,'90' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:02' ), ('3' ,'80' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:03' ), ('4' ,'70' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:04' ), ('5' ,'60' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:05' ), ('6' ,'50' ,'2021-07-12 16:50:06' ); create table t_join3( id String, star UInt8 ) ENGINE= Log; insert into t_join3 values ('1' ,'1000' ), ('2' ,'900' );
6.2 连接精度 连接精度 决定了 join 查询在连接数据时所使用的的策略,目前支持 all,any 和 asof 三种,默认 all,还可以通过 join_default_strictness 配置默认参数修改默认的连接精度类型。
对于数据是否连接匹配的判断是通过 join key 进行的,目前只支持等式 (equal join)。
交叉连接不需要使用 join key,因为它会产生笛卡尔积。
6.2.1 all
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1ALL INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘
6.2.2 any
如果左表的一行数据,在右表有多行与之连接匹配,则返回右表中的第一行数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1ANY INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘
6.2.3 asof
asof 是一种模糊连接,它允许在连接件之后追加一个定义模糊连接的匹配条件 asof_column
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate, t1.time, t2.time FROM t_join1 AS t1asof inner JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id and t1.time >= t2.time; ┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┬────────────────time ─┬─────────────t2.time─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :01 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :01 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :02 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :02 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :03 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :03 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :04 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :04 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┴─────────────────────┴─────────────────────┘
asof 还支持 使用 using 的简写形式,using 后声明的最后一个字段会被自动转换成 asof_column 模糊连接条件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate, t1.time, t2.time FROM t_join1 AS t1asof inner JOIN t_join2 AS t2 using (id,time );┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┬────────────────time ─┬─────────────t2.time─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :01 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :01 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :02 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :02 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :03 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :03 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :04 │ 2021 -07 -12 16 :50 :04 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┴─────────────────────┴─────────────────────┘
对于 asof_column 字段的使用还需要注意两点:
asof_column 必须是整数、浮点数、日期类型这类有序序列的数据类型
asof_column 不能是数据表内的唯一字段,即连接键和asof_column 不能是同一字段
6.3 连接类型 连接类型决定了 join 查询组合左右两个数据集要用的策略,他们所形成的的结果集是交集、并集、笛卡尔积或是其他形式。
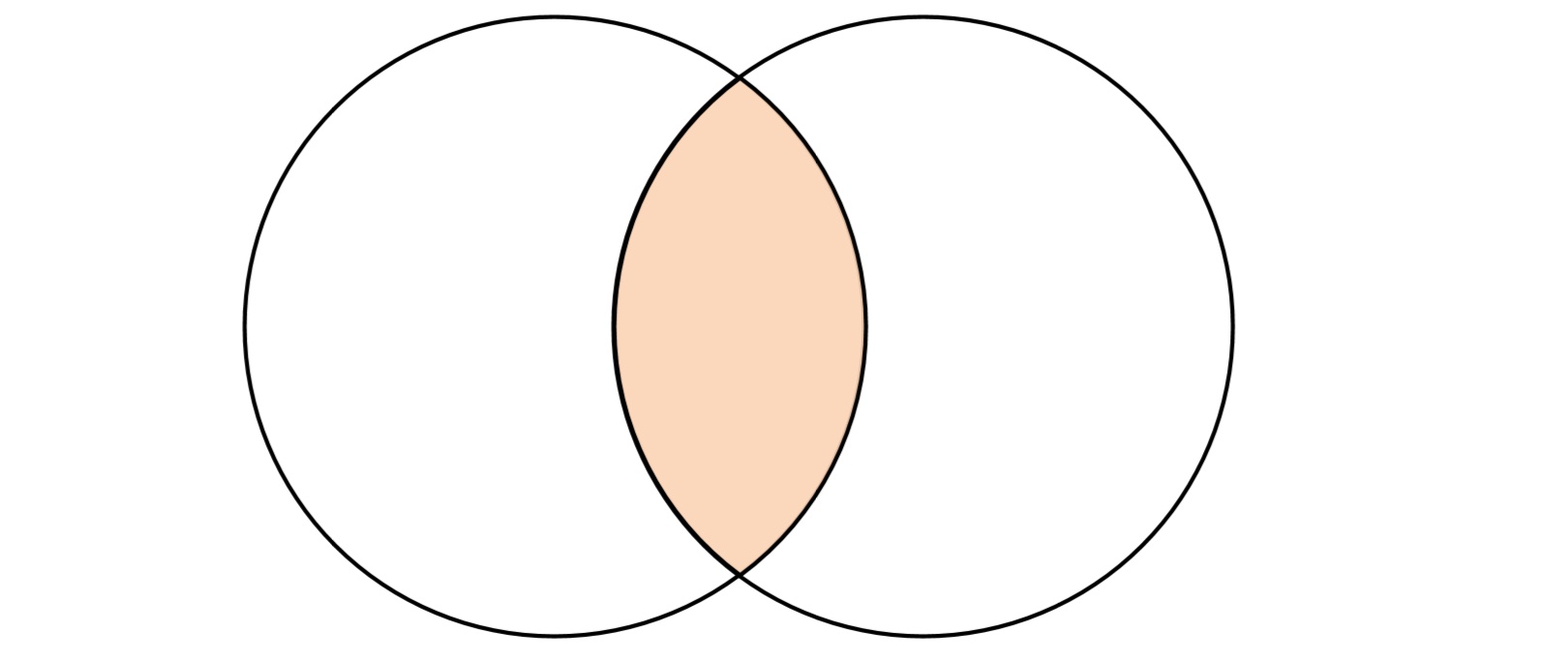
6.3.1 inner inner 表示内连接,在查询时会以左表为基础逐行遍历数据,然后从由表中找出与左边连接的行,它只会返回左右两个数据集中交集的部分,其它部分都会被排除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘
6.3.2 left [outer]
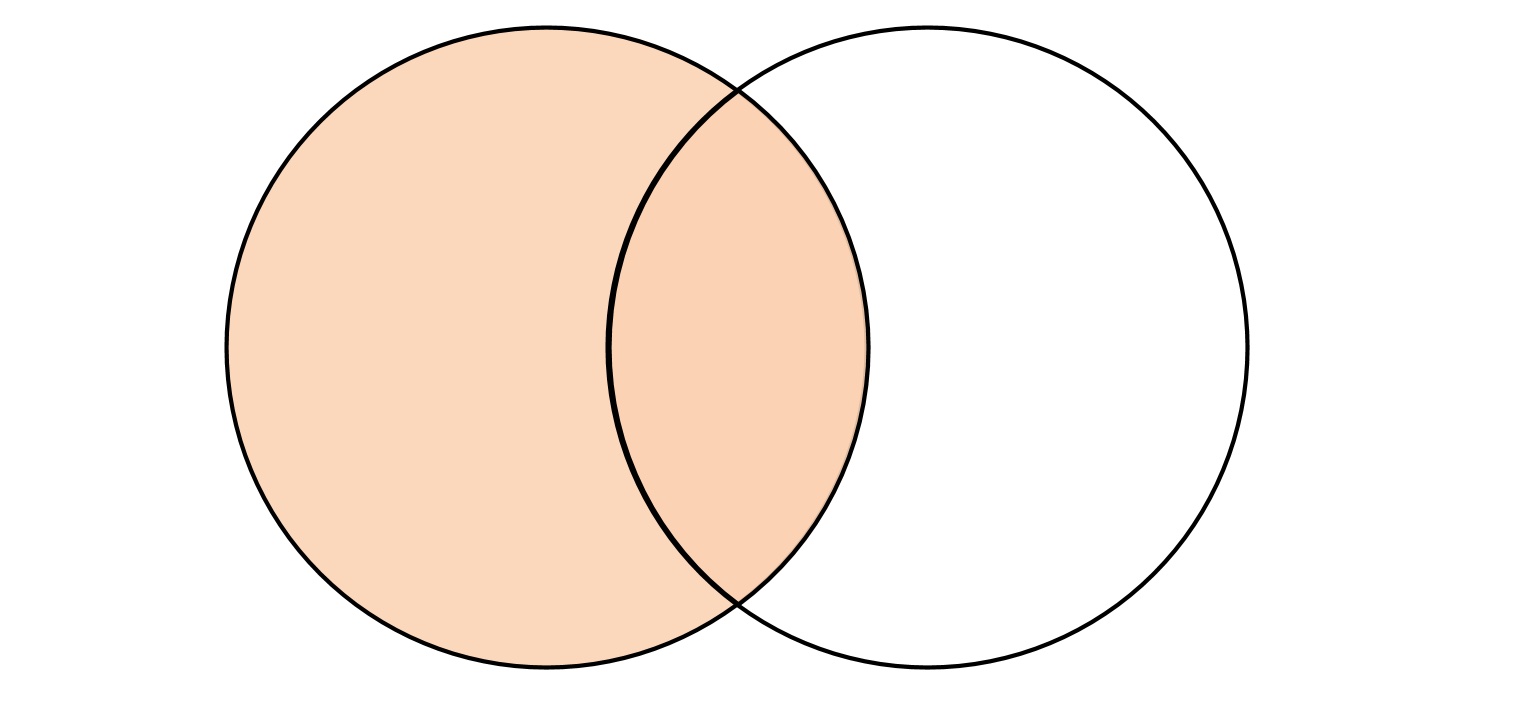
outer join 表示外连接,可以分为 left (左外连接),right(右外连接),full(全连接)三种形式,根据连接形式不同,返回的数据集合的逻辑也不相同。
在进行外连接查询时 outer 修饰符可以省略。
进行左外连接查询时,会以左表为基础,逐行遍历数据,然后从右表中找出与左边连接的行以补齐属性
如果右边没有找到连接的行,则采用响应字段数据类型的默认值填充
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1LEFT JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ │ │ clickhouse │ 0 │ │ │ spark │ 0 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘
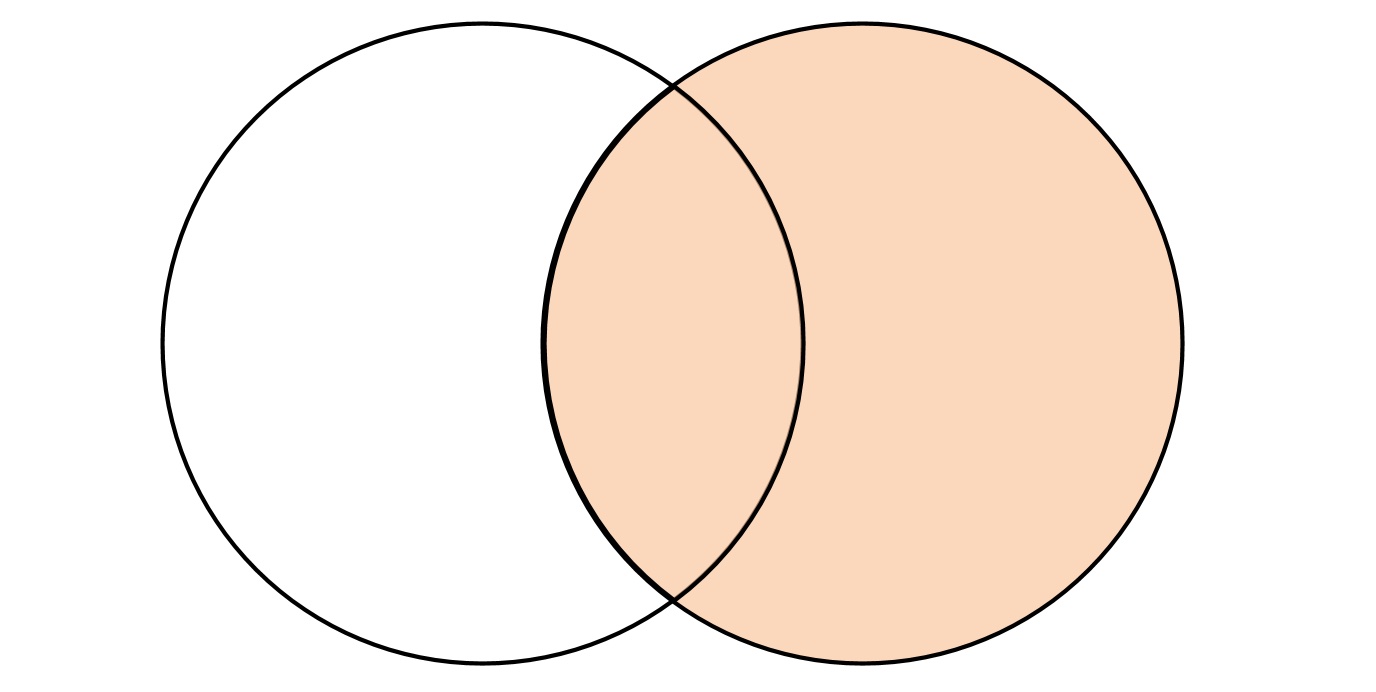
6.3.3 right [outer]
右外连接跟左外连接的逻辑刚好相反,将右表的数据全部返回,而左表不能连接的数据使用默认值补全。
在内部进行 inner join 的内部连接查询,在计算交集部分的同时,顺便记录右表中有哪些数据未能被连接
将未能连接的数据行追加到交集的尾部
将追加数据的默认值补充到未能连接的数据中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1RIGHT JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;┌─t2.id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └───────┴────────────┴──────┘ ┌─t2.id─┬─name─┬─rate─┐ │ 6 │ │ 50 │ │ 5 │ │ 60 │ └───────┴──────┴──────┘
6.3.4 full [outer]
全外连接查询会返回左右两个数据集的并集。
全连接会在内部进行类似 left join 的查询,在左外连接的过程中,顺带记录由表中已经被连接的数据
通过在由表中记录已经被连接的数据得到未被连接的数据行,
将右表中未被连接的数据行追加至结果集,并将那些数据左表中的列字段以默认值补全。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1FULL JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id;┌─t2.id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ │ │ clickhouse │ 0 │ │ │ spark │ 0 │ └───────┴────────────┴──────┘ ┌─t2.id─┬─name─┬─rate─┐ │ 6 │ │ 50 │ │ 5 │ │ 60 │ └───────┴──────┴──────┘
6.3.5 cross
cross join 表示交叉连接,它会返回左右两个数据集的笛卡尔积,也正是因为如此,cross join 不需要声明 join key,因为结果会包含他们所有的组合。
cross join 进行查询时,会以左表为基础,逐行与右表全集相乘。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1CROSS JOIN t_join2 AS t2;┌─t2.id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ clickhouse │ 90 │ │ 3 │ clickhouse │ 80 │ │ 4 │ clickhouse │ 70 │ │ 5 │ clickhouse │ 60 │ │ 6 │ clickhouse │ 50 │ │ 1 │ spark │ 100 │ │ 1 │ spark │ 95 │ ... └───────┴────────────┴──────┘
6.4 多表连接 进行多张表的连接查询时,clickhouse 会将他们转为两两连接的形式,如下查询:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate, t3.star FROM t_join1 AS t1INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.idLEFT JOIN t_join3 as t3 ON t1.id = t3.id;┌─t2.id─┬─t1.name────┬─t2.rate─┬─t3.star─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 232 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ 232 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ 132 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ 0 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ 0 │ └───────┴────────────┴─────────┴─────────┘
上面查询时,会先将 t_join1 与t_join2 进行内连接,之后再将其结果与 t_join3 进行左外连接。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate, t3.star FROM t_join1 AS t1, t_join2 AS t2 , t_join3 as t3; ┌─t2.id─┬─t1.name────┬─t2.rate─┬─t3.star─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 232 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 132 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ 232 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ 132 │ │ 2 │ clickhouse │ 90 │ 232 │ │ 2 │ clickhouse │ 90 │ 132 │ │ 3 │ clickhouse │ 80 │ 232 │ │ 3 │ clickhouse │ 80 │ 132 │ │ 4 │ clickhouse │ 70 │ 232 │ │ 4 │ clickhouse │ 70 │ 132 │ │ 5 │ clickhouse │ 60 │ 232 │ │ 5 │ clickhouse │ 60 │ 132 │ │ 6 │ clickhouse │ 50 │ 232 │ │ 6 │ clickhouse │ 50 │ 132 │ ... └───────┴────────────┴─────────┴─────────┘ SELECT t2.id, t1.name, t2.rate, t3.star FROM t_join1 AS t1, t_join2 AS t2 , t_join3 as t3 where t1.id = t2.id and t1.id = t3.id; ┌─t2.id─┬─t1.name────┬─t2.rate─┬─t3.star─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ 232 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ 232 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ 132 │ └───────┴────────────┴─────────┴─────────┘
6.5 注意事项
为了能够优化 join 查询性能,应该遵循左大右小的原则,将数据量小的表放到右侧,因为无论是哪种连接方式,右表都会被全部加载到内存中与左表进行关联。
join 查询没有缓存的支持,这意味着,每一次 join 查询,即使是连续查询相同的 SQL 语句,也都会生成一次全新的执行计划,如果应用程序会大量使用 join 查询,则需要进一步考虑借助上层应用的缓存服务或使用 join 表引擎来改善性能。
如果是在大量纬度属性补全的场景中,建议使用字典代替 jion 查询,因为在进行多表连接查询时,查询会转换成两两连接的形式,这种方式的查询很可能带来性能问题
在之前进行的连接查询中,未关联上的数据会进行默认值补充,这与其他数据库采取的策略不同,连接查询的空值策略是通过 join_use_nulls 参数指定的,默认值是 0,当参数设置为 0 时,空值由数据类型的默认值补充,当设置为 1 时,空值由 null 补充。
Join key 支持简化写法,当表的连接字段名称相同时,可以使用 using 语法简写,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 ON t1.id = t2.id┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘ SELECT t1.id, t1.name, t2.rate FROM t_join1 AS t1INNER JOIN t_join2 AS t2 using id;┌─id─┬─name───────┬─rate─┐ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 100 │ │ 1 │ clickhouse │ 95 │ │ 2 │ spark │ 90 │ │ 3 │ es │ 80 │ │ 4 │ hbase │ 70 │ └────┴────────────┴──────┘
7. where 和 prewhere 子句 where 子句基于条件表达式来实现数据过滤。如果过滤条件恰好是主键字段,则能够进一步借助索引加速查询,所以 where 子句是一条查询语句能够启用索引的判断依据(在表引擎支持索引的情况下),
1 2 3 4 select id,name,url from table where id = 'A000' (SelectExecutor): Key condition :(column 0 in ['A000' , 'A000' ])
where 表达式中包含了主键,所以它能够使用索引过滤数据区间,除了 where 之外 clickhouse 还提供了 prewhere 子句。
prewhere 只能用于 MergeTree 系列的表引擎,可以看做是对 where 的一种优化,作用于 where 相同,均是用来过滤数据。
使用 prewhere 时,只会读取 prewhere 指定的字段,用于数据过滤的条件判断,过滤完成之后再读取 select 声明的字段补充其余属性,所以 prewhere 比 where 处理的数据量更少,效率更高。
在查询时 clickhouse 会自动优化,在合适的时候将 where 替换成 prewhere,( 需要 SET optimize_move_to_prewhere = 1 )
8. group by 子句
group by 又叫聚合查询,是最常用的子句之一
group by 后面声明的表达式 通常称为聚合键,数据会按照聚合键进行聚合
clickhouse 聚合查询时,select 可以声明聚合函数和列字段,如果 select 后只声明了聚合函数,则可以省略 group by 关键字
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 SELECT sum (data_compressed_bytes) AS compressed, sum (data_uncompressed_bytes) AS uncompressed FROM system.parts┌─compressed─┬─uncompressed─┐ │ 609726471 │ 28057230433 │ └────────────┴──────────────┘
如果声明了列字段,则只能使用聚合键包含的字段,否则会报错
1 2 3 4 5 select table ,count (1 ) FROM system.parts group by table ;select table ,rows ,count (1 ) FROM system.parts group by table ;
在某些场合下可以借助 any,min,max 等集合函数来访问聚合键之外的列字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 select table ,count (1 ),any (rows ),min (rows ),max (rows ) from system.parts group by table ;┌─table ────────────────┬─count ()─┬─any (rows )─┬─min (rows )─┬─max (rows )─┐ │ t_sample │ 1 │ 5 │ 5 │ 5 │ │ t_jbod │ 1 │ 100 │ 100 │ 100 │ │ merge_column_ttl │ 1 │ 2 │ 2 │ 2 │ │ metric_log │ 148 │ 1340747 │ 6 │ 2136337 │ └──────────────────────┴─────────┴───────────┴───────────┴───────────┘
当聚合查询内的数据存在NULL 值时,clickhouse 会将 NULL 作为特定值处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 select arrayJoin([1 ,2 ,3 ,null ,null ]) as v group by v;┌────v─┐ │ 1 │ │ 2 │ │ 3 │ │ ᴺᵁᴸᴸ │ └──────┘
8.1 with rollup rollup 能够按照聚合键从右向左上卷数据,基于聚合函数一次生成分组小计和总计。如果聚合键的个数为n 个,最终会生成小计的个数为 n+1 个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 select table ,name,sum (bytes_on_disk) from system.parts group by table ,name with rollup order by table ;┌─table ──────────────────────────────────────────┬─name────────────────────────┬─sum (bytes_on_disk)─┐ │ t_merge_replace │ │ 482 │ │ t_merge_replace │ 202107 _3_3_0 │ 229 │ │ t_merge_replace │ 202106 _1_2_1 │ 253 │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴────────────────────┘
8.2 with cube cube 会像立方体模型一样,基于聚合键之间所有的组合生成小计信息,如果设置聚合键为 n ,则最终小计组合个数为 2 的 n 次方。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 select database, table , name, sum (bytes_on_disk) from ( select database, table , name, bytes_on_disk from system.parts where table = 't_merge_replace' ) group by database,table ,name with cube order by database,table ,name;┌─database─┬─table ───────────┬─name─────────┬─sum (bytes_on_disk)─┐ │ │ │ │ 482 │ │ │ │ 202106 _1_2_1 │ 253 │ │ │ │ 202107 _3_3_0 │ 229 │ │ │ t_merge_replace │ │ 482 │ │ │ t_merge_replace │ 202106 _1_2_1 │ 253 │ │ │ t_merge_replace │ 202107 _3_3_0 │ 229 │ │ db_merge │ │ │ 482 │ │ db_merge │ │ 202106 _1_2_1 │ 253 │ │ db_merge │ │ 202107 _3_3_0 │ 229 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_replace │ │ 482 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_replace │ 202106 _1_2_1 │ 253 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_replace │ 202107 _3_3_0 │ 229 │ └──────────┴─────────────────┴──────────────┴────────────────────┘
8.3 with totals 使用 totals 修饰符后,会基于聚合函数对所有数据进行汇总,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 select database,sum (bytes_on_disk),count (table ) from system.parts group by database with totals;┌─database─┬─sum (bytes_on_disk)─┬─count (table )─┐ │ query │ 271 │ 1 │ │ db1 │ 1306 │ 6 │ │ db_merge │ 4856 │ 15 │ │ system │ 635254433 │ 192 │ │ default │ 3057737 │ 2 │ └──────────┴────────────────────┴──────────────┘ Totals: ┌─database─┬─sum (bytes_on_disk)─┬─count (table )─┐ │ │ 638318603 │ 216 │ └──────────┴────────────────────┴──────────────┘
9. having having 子句需要依赖 group by 使用,它能够在聚合计算之后实现二次过滤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 EXPLAIN SELECT count (1 ) FROM system.partsGROUP BY database┌─explain───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Expression ((Projection + Before ORDER BY )) │ │ Aggregating │ │ Expression (Before GROUP BY ) │ │ SettingQuotaAndLimits (Set limits and quota after reading from storage) │ │ ReadFromStorage (SystemParts) │ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ EXPLAIN SELECT count (1 ) FROM system.partsGROUP BY databasehaving table = 't_merge_replace' ┌─explain─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Expression ((Projection + Before ORDER BY )) │ │ Aggregating │ │ Expression (Before GROUP BY ) │ │ Filter (WHERE ) │ │ SettingQuotaAndLimits (Set limits and quota after reading from storage) │ │ ReadFromStorage (SystemParts) │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ EXPLAIN SELECT count (1 ) FROM ( SELECT database FROM system.parts WHERE table = 't_merge_replace' ) GROUP BY database┌─explain─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Expression ((Projection + Before ORDER BY )) │ │ Aggregating │ │ Expression ((Before GROUP BY + (Projection + Before ORDER BY ))) │ │ Filter (WHERE ) │ │ SettingQuotaAndLimits (Set limits and quota after reading from storage) │ │ ReadFromStorage (SystemParts) │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
having 子句经常用在我们要过滤聚合后的数据的情况,比如按照 table 聚合,过滤出聚合数值大于 1000000 字节的表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 SELECT table , sum (bytes_on_disk) AS total FROM system.partsGROUP BY table HAVING total > 1000000 ┌─table ───────────────────┬─────total─┐ │ metric_log │ 606119816 │ │ t_hot_to_cold │ 3057506 │ │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 31422436 │ └─────────────────────────┴───────────┘
10. order by order by 子句通过声明排序键来指定查询数据返回时的顺序,在 mergeTree 表引擎中也有 order by 参数用于指定排序键,MergeTree 中指定排序键后,数据在各个分区内会按照定对的规则排序,这是一种分区内的局部排序,如果在查询时跨越了多个分区,则返回结果数据的顺序是未知的,每次查询结果可能都不相同,如果想对结果进行排序,就需要在查询时使用 order by 子句 来实现全局排序。
order by 在使用时,可以定义多个排序键,每个排序键可以跟 ASC(升序)或 DESC(降序) 来确定排序顺序,如果不写则默认升序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 select arrayJoin([1 ,2 ,3 ]) as v1,arrayJoin([4 ,5 ,6 ]) as v2 order by v1 ASC ,v2 DESC ;┌─v1─┬─v2─┐ │ 1 │ 6 │ │ 1 │ 5 │ │ 1 │ 4 │ │ 2 │ 6 │ │ 2 │ 5 │ │ 2 │ 4 │ │ 3 │ 6 │ │ 3 │ 5 │ │ 3 │ 4 │ └────┴────┘ select arrayJoin([1 ,2 ,3 ]) as v1,arrayJoin([4 ,5 ,6 ]) as v2 order by v1 ,v2 DESC ;┌─v1─┬─v2─┐ │ 1 │ 6 │ │ 1 │ 5 │ │ 1 │ 4 │ │ 2 │ 6 │ │ 2 │ 5 │ │ 2 │ 4 │ │ 3 │ 6 │ │ 3 │ 5 │ │ 3 │ 4 │ └────┴────┘ select arrayJoin([1 ,2 ,3 ]) as v1,arrayJoin([4 ,5 ,6 ]) as v2 order by v1 DESC ,v2 DESC ;┌─v1─┬─v2─┐ │ 3 │ 6 │ │ 3 │ 5 │ │ 3 │ 4 │ │ 2 │ 6 │ │ 2 │ 5 │ │ 2 │ 4 │ │ 1 │ 6 │ │ 1 │ 5 │ │ 1 │ 4 │ └────┴────┘
10.1 nulls last NULL 值排在最后,这也是默认行为,修饰符可以省略,在这种情况下,数据排序为:其他值 > NaN > NULL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 with arrayJoin([20 ,null ,32.3 ,0 / 0 ,1 / 0 ,-1 / 0 ]) as v1select v1┌───v1─┐ │ 20 │ │ ᴺᵁᴸᴸ │ │ 32.3 │ │ nan │ │ inf │ │ - inf │ └──────┘ with arrayJoin([20 ,null ,32.3 ,0 / 0 ,1 / 0 ,-1 / 0 ]) as v1select v1 order by v1 desc nulls last ;┌───v1─┐ │ inf │ │ 32.3 │ │ 20 │ │ - inf │ │ nan │ │ ᴺᵁᴸᴸ │ └──────┘ with arrayJoin([20 ,null ,32.3 ,0 / 0 ,1 / 0 ,-1 / 0 ]) as v1select v1 order by v1 desc ;┌───v1─┐ │ inf │ │ 32.3 │ │ 20 │ │ - inf │ │ nan │ │ ᴺᵁᴸᴸ │ └──────┘
10.2 nulls first NULL 值排在最前面,这情况下 数据的排序顺序为:NULL > NaN > 其他值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 with arrayJoin([20 ,null ,32.3 ,0 / 0 ,1 / 0 ,-1 / 0 ]) as v1select v1 order by v1 desc nulls first ;┌───v1─┐ │ ᴺᵁᴸᴸ │ │ nan │ │ inf │ │ 32.3 │ │ 20 │ │ - inf │ └──────┘
11. limit by
limit by 子句和 limit 有所不同,它运行在 order by 之后 和 limit 之前,能够按照指定分组,返回前 n 行数据,如果数据少于 n 行则按实际数量返回。
limit by 子句常用于 top N 场景。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 SELECT database, table , sum (bytes_on_disk) AS bytes FROM system.partsGROUP BY database, table ORDER BY database DESC , bytes DESC LIMIT 2 BY database ┌─database─┬─table ───────────────────┬─────bytes─┐ │ system │ metric_log │ 479773421 │ │ system │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 31669444 │ │ query │ t_sample │ 271 │ │ default │ t_hot_to_cold │ 3057506 │ │ default │ insert_test │ 231 │ │ db_merge │ t_jbod │ 779 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_tree_partition │ 672 │ │ db1 │ t_partition │ 465 │ │ db1 │ t_partition_default │ 390 │ └──────────┴─────────────────────────┴───────────┘
1 ORDER BY col1 DESC LIMIT 2 BY col1,col2
limit by 也支持跳过 offset 偏移量获取数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 limit n offset y by express limit y,n by express SELECT database, table , max (bytes_on_disk) AS bytes FROM system.partsGROUP BY database, table ORDER BY bytes DESC LIMIT 1 , 3 BY database ┌─database─┬─table ───────────────────┬───bytes─┐ │ system │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 8388674 │ │ system │ query_log │ 202273 │ │ system │ query_thread_log │ 186276 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum_nested │ 438 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum │ 407 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_agg │ 362 │ │ db1 │ t_partition │ 233 │ │ db1 │ t_partition_default │ 232 │ │ default │ insert_test │ 231 │ │ db1 │ alter_add_column │ 218 │ └──────────┴─────────────────────────┴─────────┘ SELECT database, table , max (bytes_on_disk) AS bytes FROM system.partsGROUP BY database, table ORDER BY bytes DESC LIMIT 3 BY database ┌─database─┬─table ───────────────────┬────bytes─┐ │ system │ metric_log │ 97797533 │ │ system │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 8388674 │ │ default │ t_hot_to_cold │ 3057506 │ │ system │ query_log │ 202273 │ │ db_merge │ t_jbod │ 779 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum_nested │ 438 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum │ 407 │ │ query │ t_sample │ 271 │ │ db1 │ t_partition_b │ 233 │ │ db1 │ t_partition │ 233 │ │ db1 │ t_partition_default │ 232 │ │ default │ insert_test │ 231 │ └──────────┴─────────────────────────┴──────────┘
12. limit
limit 子句用于返回指定的前 n 行数据,常用于分页场景。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 limit n limit n offset y limit y,n select number from system.numbers limit 5 ;┌─number─┐ │ 0 │ │ 1 │ │ 2 │ │ 3 │ │ 4 │ └────────┘ select number from system.numbers limit 5 offset 3 ;┌─number─┐ │ 3 │ │ 4 │ │ 5 │ │ 6 │ │ 7 │ └────────┘ select number from system.numbers limit 3 ,5 ;┌─number─┐ │ 3 │ │ 4 │ │ 5 │ │ 6 │ │ 7 │ └────────┘
limit 子句可以和 limit by 一起使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 SELECT database, table , max (bytes_on_disk) AS bytes FROM system.partsGROUP BY database, table ORDER BY bytes DESC LIMIT 1 , 3 BY database ┌─database─┬─table ───────────────────┬───bytes─┐ │ system │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 8388674 │ │ system │ query_log │ 202273 │ │ system │ query_thread_log │ 186276 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum_nested │ 438 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_sum │ 407 │ │ db_merge │ t_merge_agg │ 362 │ │ db1 │ t_partition │ 233 │ │ db1 │ t_partition_default │ 232 │ │ default │ insert_test │ 231 │ │ db1 │ alter_add_column │ 218 │ └──────────┴─────────────────────────┴─────────┘ SELECT database, table , max (bytes_on_disk) AS bytes FROM system.partsGROUP BY database, table ORDER BY bytes DESC LIMIT 1 , 3 BY database LIMIT 3 ┌─database─┬─table ───────────────────┬───bytes─┐ │ system │ asynchronous_metric_log │ 8388674 │ │ system │ query_log │ 202273 │ │ system │ query_thread_log │ 186276 │ └──────────┴─────────────────────────┴─────────┘
在使用 limit 查询数据跨越多个分区的时候,在没有是有 order by 进行全局排序的情况下,每次 limit 查询返回的数据可能有所不同,所以建议搭配 order by 一起使用。
13. select
select 子句决定了一次查询语句最终返回哪些字段或表达式,虽然 select 语句位于 SQL 语句的起始位置,但是它确实在一众句子之后执行的。在其它子句执行以后,select 会将选取的字段或表达式作用于每一行数据。
如果使用通配符 * 则返回数据表的所有字段,但是作为列式数据库的clickhouse,并不建议这么做。
clickhouse 还提供了基于正则表达式查询的形式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 SELECT COLUMNS('^n' ), COLUMNS('p' ) FROM system.databasesLIMIT 2 ┌─name─┬─data_path──────────────────┬─metadata_path───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ db1 │ / var/ lib/ clickhouse/ store/ │ / var/ lib/ clickhouse/ store/ 1 b6/ 1 b63d246- d32d-45 f1- a6eb-553 dde05598b/ │ │ db2 │ / var/ lib/ clickhouse/ store/ │ / var/ lib/ clickhouse/ store/ 47 c/ 47 c94419-6675 -4861 - a5f5- c76cb0b2acc2/ │ └──────┴────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
14. distinct
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 create table t_distinct( name String, value UInt8 )ENGINE= TinyLog; insert into t_distinct values ('a' ,1 ), ('a' ,2 ), ('b' ,1 ), ('b' ,3 ), ('c' ,3 ); select distinct name from t_distinct;┌─name─┐ │ a │ │ b │ │ c │ └──────┘
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 EXPLAIN SELECT DISTINCT nameFROM t_distinct;┌─explain─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Expression (Projection) │ │ Distinct │ │ Distinct (Preliminary DISTINCT ) │ │ Expression (Before ORDER BY ) │ │ SettingQuotaAndLimits (Set limits and quota after reading from storage) │ │ ReadFromStorage (TinyLog) │ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ EXPLAIN SELECT nameFROM t_distinctGROUP BY name;┌─explain───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ Expression ((Projection + Before ORDER BY )) │ │ Aggregating │ │ Expression (Before GROUP BY ) │ │ SettingQuotaAndLimits (Set limits and quota after reading from storage) │ │ ReadFromStorage (TinyLog) │ └───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
distinct 与 group by 可以同时使用,如果使用了 limit 且没有 order by 子句,则 distinct 在满足条件时能够迅速结束查询,这样可以避免多余处理逻辑,当 distinct 与 group by 同时使用时,执行优先级是先 distinct 后 order by。
15. union all
union all 子句能够联合左右两边的两组查询,将结果合并一起返回,在一次查询中可以声明多次 union all 以便联合多组查询。
union all 子句两侧的查询必须做到字段数量和字段类型一致,否则无法将数据联合到一起,
union all 子句两侧的查询的字段名可以不同,查询结果会以左侧表的字段名为准
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 select name,value from t_distinct limit 2 union all select name,value from t_distinct limit 2 union all select name,value from t_distinct limit 2 ;┌─name─┬─value ─┐ │ a │ 1 │ │ a │ 2 │ └──────┴───────┘ ┌─name─┬─value ─┐ │ a │ 1 │ │ a │ 2 │ └──────┴───────┘ ┌─name─┬─value ─┐ │ a │ 1 │ │ a │ 2 │ └──────┴───────┘