1. 介绍
在Java中,static是一个关键字,用于修饰类、方法和变量。使用static关键字声明的成员属于类级别,不需要实例化对象就可以访问和使用。在类定义中使用static关键字声明的变量可以作为常量使用。
2. 为什么设计 static 关键字
提出问题的主要目的就是让大家思考解决之道,从而引出我们要讲的知识点。
说有一群小孩在玩堆雪人,不定时有新的小孩加入,请问如何之道现在共有多少人在玩,编写程序解决问题。
- 先使用之前学过的技术解决
- 思路: 在main方法中定义一个变量count
- 当有一个小孩加入游戏后, count++, count就记录了有多少小孩, 如果想知道有多少人在玩游戏, 打印count值即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class ChildrenGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
Chlind c1 = new Chlind("小明");
count++;
c1.join();
Chlind c2 = new Chlind("小红");
count++;
c2.join();
System.out.println("现在共有 "+count+ "个小朋友玩堆雪人") ;
}
}
class Chlind{
private String name;
public Chlind(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void join(){
System.out.println(this.name+" 参加游戏");
}
}
|
count 是一个独立的变量, 没有使用到面向对象
如果以后访问count很麻烦,比如问一个小朋友现在有多少人, 他就不知道
如果设计一个 count变量,我们在创建一个小孩时,就把count +++ 并且count是对所有对象共享的就OK了,我们可以使用类变量来解决这个问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class ChildrenGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child02 c1 = new Child02("小明");
c1.count++;
c1.join();
Child02 c2 = new Child02("小红");
c2.count++;
c2.join();
System.out.println("现在共有 "+Child02.count+ "个小朋友玩堆雪人") ;
}
}
class Child02 {
public static int count;
private String name;
public Child02(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void join(){
System.out.println(this.name+" 参加游戏");
}
}
|
类变量(静态/static变量)是用一个类所有对象共享的,
类变量在类加载的时候就生成了
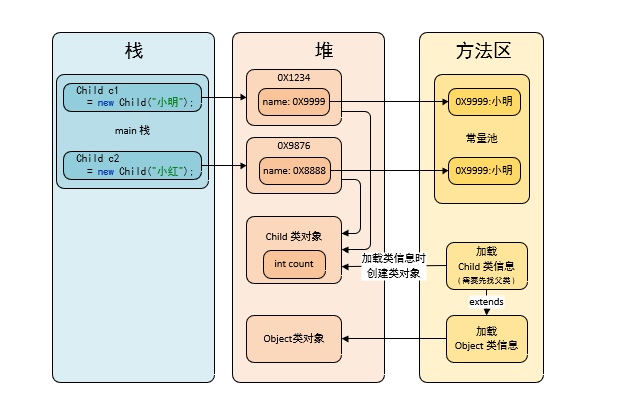
注意 在jdk1.7 之前静态变量存储在方法区中的静态域中
3. 类变量和类方法
类变量也叫静态变量/静态属性,是该类的所有对象共享的变量,任何一个该类的对象去访问它时,取到的都是相同的值, 同样任何一个该类的对象去修改它时,修改的也是同一个变量。
1
2
| 访问修饰符 static 数据类型 变量名称;
static 访问修饰符 数据类型 变量名称;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class Visit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Person03.public_);
System.out.println(Person03.protected_);
System.out.println(Person03.default_);
Person03 person = new Person03();
System.out.println(person.public_);
System.out.println(person.protected_);
System.out.println(person.default_);
}
}
class Person03{
public static String public_ = "publicVariable";
protected static String protected_ = "protectedVariable";
static String default_ = "defaultVariable";
private static String private_ = "privateVariable";
}
|
4. 类变量和类方法
- 什么时候需要使用类变量
当我们需要让某个类的所有对象都共享一个变量是,就可以考虑使用类变量,比如定义学生类, 统计学生一共交了多少钱
1
2
3
4
| class Student{
String name;
static double fee;
}
|
- 类变量与成员变量的区别?
类变量是该类的所有对象共享的, 而成员变量是每个对象特有的
定义变量时加上 static 修饰的变量即为类变量, 否则即为普通变量/成员变量
类变量可以通过 类名.类变量 或 对象名.类变量 访问, 通常会使用 类名.类变量 来访问,
成员变量只能通过 对象名.成员变量名 来访问
类变量在类加载时就已经初始化了, 也就是说即使没有实例化对象, 只要加载了类, 就可以使用类变量了
类变量的声明周期是随着类的加载开始, 随着类的销毁结束
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class Static04_visit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(A04.a);
}
}
class A04{
public static int a = 100;
}
|
5. 类方法
类方法也叫静态方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| 访问修饰符 static 数据类型 方法名称(形参列表){
方法体;
}
static 访问修饰符 数据类型 方法名称(形参列表){
方法体;
}
public static void aa(){
int a = 1+1;
}
static public void bb(){
int a = 1+1;
}
|
静态方法可以通过 类名.静态方法名 或 对象名.静态方法名 访问, 通常会使用 类名.静态方法名 来访问,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Static05_method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stu05 s1 = new Stu05("小明");
s1.addFee(100);
Stu05 s2 = new Stu05("小明");
s2.addFee(300);
Stu05.showFee();
}
}
class Stu05{
private String name;
private static double fee;
public static void addFee(double fee){
Stu05.fee +=fee;
}
public static void showFee(){
System.out.println("总费用为:"+ fee);
}
public Stu05(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
|
6. 类方法使用场景
当类方法中不涉及任何和对象相关的成员, 则可以将方法设计成静态方法, 提高开发效率
比如:Math、Arrays、collections工具类中的方法
在实际开发中, 往往会用到一些通用的方法, 设计成静态方法, 这样我们不需要创建对象就可以使用他们, 比如打印一维数组, 冒泡排序完成某个计算任务等等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class Static06_utils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("12 + 15 = "+ Utils.sum(12,15));
System.out.println("9 开平方结果是:" + Math.sqrt(9));
}
}
class Utils{
public static int sum(int d1,int d2){
return d1+d2;
}
}
|
7. 类变量与类方法
- 类方法和普通方法都是随着类的加载而加载,将结果存储在方法区,
类方法中无this的参数
普通方法中引航者this参数
- 类方法可以通过类名调用, 也可以通过对象名调用
- 普通方法和对象有关,需要通过对象名调用,比如
对象名.方法名(实参列表) 不能通过类名调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Person07{
private String name;
private static String age;
public static void eat(){
System.out.println("eating . . .");
}
public static void run(){
System.out.println(age);
eat();
}
}
|
- 静态方法中不允许使用和对象有关的关键字,比如 this、super。 普通方法可以使用这些关键字
- 在遵守访问权限的前提下,静态方法中只能访问静态变量和静态方法
- 在遵守访问权限的前提下,普通成员方法既可以访问静态方法、静态变量, 也可以访问非静态方法、非静态变量
8. main 方法
解释main方法的形式,
1
2
3
4
|
public static void main(String args[]){
}
|
main方法是在虚拟机调用
java虚拟机需要调用类的main方法, 所以改方法必须是public 级别
java虚拟机在执行main()方法时不必创建对象, 所以该方法必须是static级别的
该方法接受String类型的数组, 该数组中保存执行java命令时所传递给所运行的类的参数,
参数传递方式 java 执行程序 参数1 参数2 参数3
- 特别提示
- 在main方法中, 我们可以直接调用main方法所在类的静态方法或静态属性
- 但是, 不能直接访问该类中的非静态成员, 必须创建该类的一个实例后, 才能通过这个对象访问非静态成员
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| class Main11{
public static void m1(){
System.out.println("Main11 静态方法");
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println("Main11 非静态方法");
}
public static int v1 = 100;
public int v2 = 100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(v1);
m1();
Main11 m = new Main11();
System.out.println(m.v1);
System.out.println(m.v2);
m.m1();
m.m2();
}
}
|


