1. Flink State 介绍 1.1 什么是 State(状态)
由一个任务维护,并且用来计算某个结果的所有数据,就属于这个任务的状态
可以认为状态就是一个本地变量,可以被任务的业务逻辑访问
当任务失败时,可以使用状态恢复数据
状态始终是与特定算子相关联的。
算子需要预先注册其状态,以便在Flink运行时能够了解算子状态
Flink 会进行状态的管理,包括状态一致性、故障处理以及高效的存储和访问,以便开发人员可以专注于应用的业务逻辑。
Flink 内置的很多算子,数据源 source,数据存储 sink 都是有状态的,流中的数据都是 buffer records,会保存一定的元素或者元数据。例如: ProcessWindowFunction 会缓存输入流的数据,ProcessFunction 会保存设置的定时器信息等等。
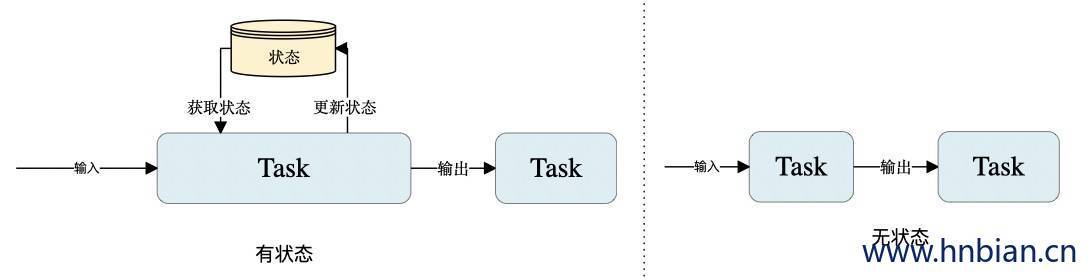
1.2 有状态与无状态的计算 流式计算分为无状态 和有状态 两种情况。
下图展示了 无状态流处理 和 有状态流处理 的 主要区别。无状态流处理分别接收每条数据记录,然后根据最新输入的数据生成输出数据。有状态流处理会维护状态,并基于最新输入的记录和当前的状态值生成输出记录。
尽管无状态的计算很重要,但是流处理对有状态的计算更感兴趣。事实上,正确地实现有状态的计算比实现无状态的计算难得多。旧的流处理系统并不支持有状态的计算,而新一代的流处理系统则将状态及其正确性视为重中之重。
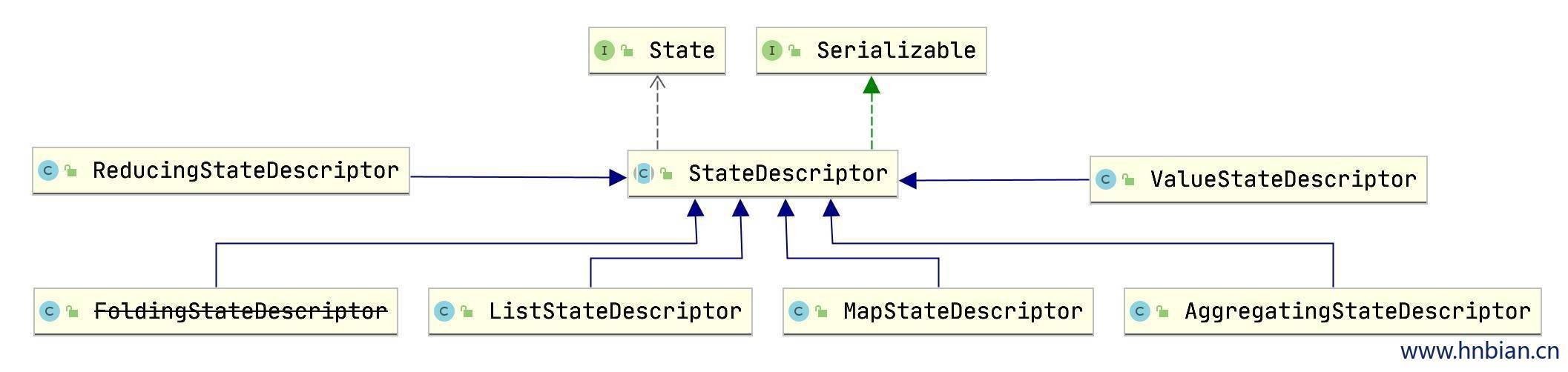
2. 状态描述(StateDescriptor) StateDescriptor 是所有状态描述符的基类。 Flink 通过 StateDescriptor 定义状态,包括状态的名称,存储数据的类型,序列化器等基础信息。
2.1 StateDescriptor 种类
使用不同类型的 StateDescriptor 可以创建出不同类型的状态,flink 中提供了 ListStateDescriptor、MapStateDescriptor、ValueStateDescriptor、AggregatingStateDescriptor、ReducingStateDescriptor 、FoldingStateDescriptor(废弃) 状态描述符供使用。他们都继承自 StateDescriptor。
2.2 StateDescriptor源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 public abstract class StateDescriptor<S extends State , T> implements Serializable private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory .getLogger(StateDescriptor .class ); public enum Type { UNKNOWN ,VALUE ,LIST ,REDUCING ,FOLDING ,AGGREGATING ,MAP } private static final long serialVersionUID = 1 L; protected final String name; private final AtomicReference <TypeSerializer <T >> serializerAtomicReference = new AtomicReference <>(); @Nullable private TypeInformation <T > typeInfo; @Nullable private String queryableStateName; @Nonnull private StateTtlConfig ttlConfig = StateTtlConfig .DISABLED ; @Nullable protected transient T defaultValue; protected StateDescriptor (String name,TypeSerializer <T > serializer, @Nullable T defaultValue) { this .name = checkNotNull(name, "name must not be null" ); this .serializerAtomicReference.set( checkNotNull(serializer, "serializer must not be null" ) ); this .defaultValue = defaultValue; } protected StateDescriptor (String name, TypeInformation <T > typeInfo, @Nullable T defaultValue) { this .name = checkNotNull(name, "name must not be null" ); this .typeInfo = checkNotNull(typeInfo, "type information must not be null" ); this .defaultValue = defaultValue; } protected StateDescriptor (String name, Class <T > type , @Nullable T defaultValue ) this .name = checkNotNull(name, "name must not be null" ); checkNotNull(type , "type class must not be null ") try { this .typeInfo = TypeExtractor .createTypeInfo(type ) } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException ( "Could not create the type information for '" + type .getName() + "'. " + "The most common reason is failure to infer the generic type information, due to Java's type erasure. " + "In that case, please pass a 'TypeHint' instead of a class to describe the type. " + "For example, to describe 'Tuple2<String, String>' as a generic type, use " + "'new PravegaDeserializationSchema<>(new TypeHint<Tuple2<String, String>>(){}, serializer);'" , e); } this .defaultValue = defaultValue; } public String getName() { return name; } public T getDefaultValue() { if (defaultValue != null ) { TypeSerializer <T > serializer = serializerAtomicReference.get(); if (serializer != null ) { return serializer.copy(defaultValue); } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("Serializer not yet initialized." ); } } else { return null ; } } public TypeSerializer <T > getSerializer() { TypeSerializer <T > serializer = serializerAtomicReference.get(); if (serializer != null ) { return serializer.duplicate(); } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("Serializer not yet initialized." ); } } @VisibleForTesting final TypeSerializer <T > getOriginalSerializer() { TypeSerializer <T > serializer = serializerAtomicReference.get(); if (serializer != null ) { return serializer; } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("Serializer not yet initialized." ); } } public void setQueryable(String queryableStateName) { Preconditions .checkArgument( ttlConfig.getUpdateType() == StateTtlConfig .UpdateType .Disabled , "Queryable state is currently not supported with TTL" ); if (this .queryableStateName == null ) { this .queryableStateName = Preconditions .checkNotNull(queryableStateName, "Registration name" ); } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("Queryable state name already set" ); } } @Nullable public String getQueryableStateName() { return queryableStateName; } public boolean isQueryable() { return queryableStateName != null ; } public void enableTimeToLive(StateTtlConfig ttlConfig) { Preconditions .checkNotNull(ttlConfig); Preconditions .checkArgument( ttlConfig.getUpdateType() != StateTtlConfig .UpdateType .Disabled && queryableStateName == null , "Queryable state is currently not supported with TTL" ); this .ttlConfig = ttlConfig; } @Nonnull @Internal public StateTtlConfig getTtlConfig() { return ttlConfig; } public boolean isSerializerInitialized() { return serializerAtomicReference.get() != null ; } public void initializeSerializerUnlessSet(ExecutionConfig executionConfig) { if (serializerAtomicReference.get() == null ) { checkState(typeInfo != null , "no serializer and no type info" ); TypeSerializer <T > serializer = typeInfo.createSerializer(executionConfig); if (!serializerAtomicReference.compareAndSet(null , serializer)) { LOG .debug("Someone else beat us at initializing the serializer." ); } } } @Override public final int hashCode() { return name.hashCode() + 31 * getClass().hashCode(); } @Override public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this ) { return true ; } else if (o != null && o.getClass() == this .getClass()) { final StateDescriptor <?, ?> that = (StateDescriptor <?, ?>) o; return this .name.equals(that.name); } else { return false ; } } @Override public String toString() { return getClass().getSimpleName() + "{name=" + name + ", defaultValue=" + defaultValue + ", serializer=" + serializerAtomicReference.get() + (isQueryable() ? ", queryableStateName=" + queryableStateName + "" : "" ) + '}'; } public abstract Type getType(); private void writeObject(final ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException { out.defaultWriteObject(); if (defaultValue == null ) { out.writeBoolean(false ); } else { TypeSerializer <T > serializer = serializerAtomicReference.get(); checkNotNull(serializer, "Serializer not initialized." ); out.writeBoolean(true ); byte[] serializedDefaultValue; try (ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); DataOutputViewStreamWrapper outView = new DataOutputViewStreamWrapper (baos)) { TypeSerializer <T > duplicateSerializer = serializer.duplicate(); duplicateSerializer.serialize(defaultValue, outView); outView.flush(); serializedDefaultValue = baos.toByteArray(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new IOException ("Unable to serialize default value of type " + defaultValue.getClass().getSimpleName() + "." , e); } out.writeInt(serializedDefaultValue.length); out.write(serializedDefaultValue); } } private void readObject(final ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException , ClassNotFoundException { in.defaultReadObject(); boolean hasDefaultValue = in.readBoolean(); if (hasDefaultValue) { TypeSerializer <T > serializer = serializerAtomicReference.get(); checkNotNull(serializer, "Serializer not initialized." ); int size = in.readInt(); byte[] buffer = new byte[size]; in.readFully(buffer); try (ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream (buffer); DataInputViewStreamWrapper inView = new DataInputViewStreamWrapper (bais)) { defaultValue = serializer.deserialize(inView); } catch (Exception e) { throw new IOException ("Unable to deserialize default value." , e); } } else { defaultValue = null ; } } }
2.3 StateDescriptor 分类
ListStateDescriptor:可用于描述 ListState 类型状态
MapStateDescriptor:可用于描述 MapState 类型状态
ValueStateDescriptor:可用于描述 ValueState 类型状态
AggregatingStateDescriptor:可用于描述 AggregatingState 类型状态
ReducingStateDescriptor:可用于描述 ReducingState 类型状态
3. 状态的分类 3.1 Managed State 和 Raw State Flink 状态主要分为托管状态(Managed State)和原始状态(Raw State)。托管状态是由 Flink 自动管理的,这包括状态的存储、恢复以及优化等操作。托管状态包括值状态(Value State),列表状态(List State),映射状态(Map State)等类型,这些类型的状态在 Flink 的检查点和保存点机制中,Flink 会负责处理这些状态的快照和恢复。
相反,原始状态(Raw State)是由用户管理的,用户需要自己定义状态的序列化和反序列化过程。这通常适用于一些特殊的情况,例如用户需要自定义序列化机制,或者需要对状态的存储和恢复有更精细的控制。虽然用户需要自己处理状态的序列化和反序列化,但 Flink 仍然提供了一些基础的支持和接口,以帮助用户更好地处理原始状态。
-
Managed State
Raw State
状态管理方式
由 Flink Runtime 托管,状态是自动存储、自动恢复的
用户自定义的状态,自己管理
状态数据结构
常用的数据结构,如ValueState、ListState、MapState
字节数组,byte[]
状态使用场景
绝大多数 Flink 算子都可以使用
用户自定义算子
通常在 DataStream 上的状态推荐使用托管的状态,当实现一个用 户自定义的operator时,会使用到原始状态。
3.2 Operator State 和 Keyed State
Flink 的状态主要分为两种类型:Operator State 和 Keyed State。
Operator State :Operator State 是每个并行操作符实例的私有状态,它是在分布式计算中一个任务的本地状态。比如说,我们在做数据重平衡时,就会用到 Operator State,因为这个过程中需要对数据进行缓存,并在适当的时候进行释放。如果一个流计算任务由多个并行子任务组成,每个子任务都会有一个独立的 Operator State。对于 Operator State,Flink 并不知道其内部的数据结构,只负责其存储和恢复。Keyed State :Keyed State 是当在 KeyedStream 上运行操作符时使用的状态。在 Flink 中,Keyed State 是绑定到数据流中的特定键(Key)的。这意味着 Flink 维护了数据流中每一个 key 的状态。当处理一个新的元素时,Flink 会将状态的键设置为该元素的键,然后调用对应的处理函数。Keyed State 的一个典型应用场景是计算每个键的滚动聚合。
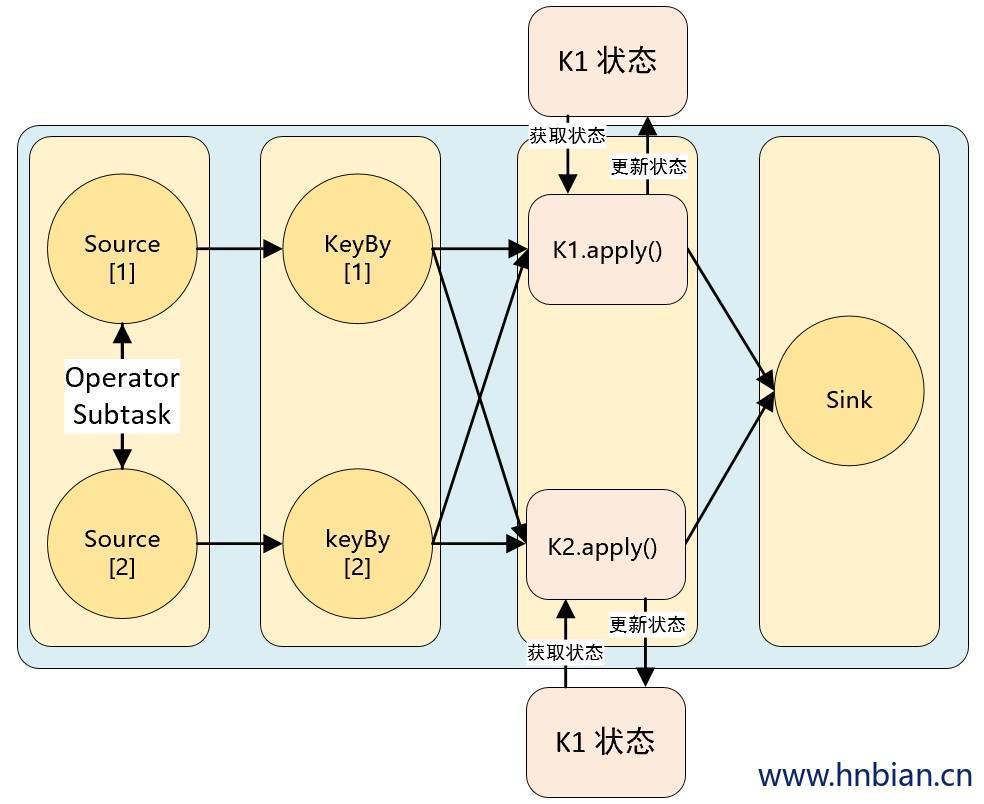
3.2.1 Keyed State 介绍 Keyed State(键控状态)是根据输入数据流中定义的键(key)来维护和访问的。Flink 为每个键值维护一个状态实例,并将具有相同键的所有数据,都分区到同一个算子任务中,这个任务会维护和处理这个key 对应的状态。当任务处理一条数据时,它会自动将状态的访问范围限定为当前数据的 key。因此,具有相同 key 的所有数据都会访问相同的状态。Keyed State 很类似于一个分布式的 key-value map 数据结构,只能用于 KeyedStream( keyBy 算子处理之后)。
Keyed State 有五种类型:
ValueState :值状态,保存单个类型为 T 的值
ListState :列表状态,保存一个类型为 T 的列表
MapState :映射状态,保存 Key-Value 对
ReducingState :聚合状态
AggregatingState:聚合状态
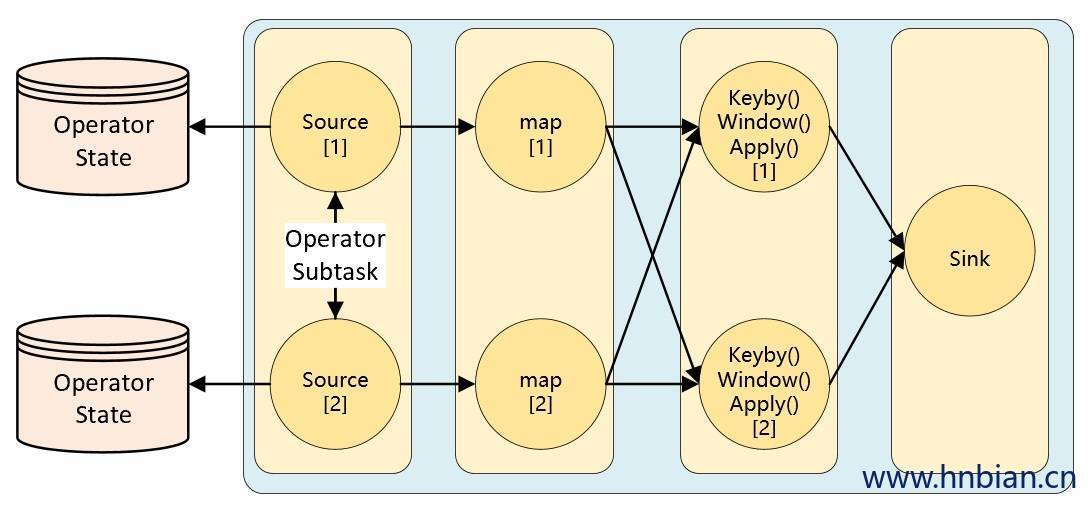
3.2.2 Operator State 介绍 KeyedState 是在进行 KeyBy 之后进行状态操作时使用的状态类型,那么像 Source、Sink算子是不会进行 KeyBy 操作的,当这类算子也需要用到状态,应该怎么操作呢?这时候就需要使用 Operator State(算子状态 )。Operator State 是绑定在 Operator 的并行度实例上的,也就是说一个并行度一个状态。
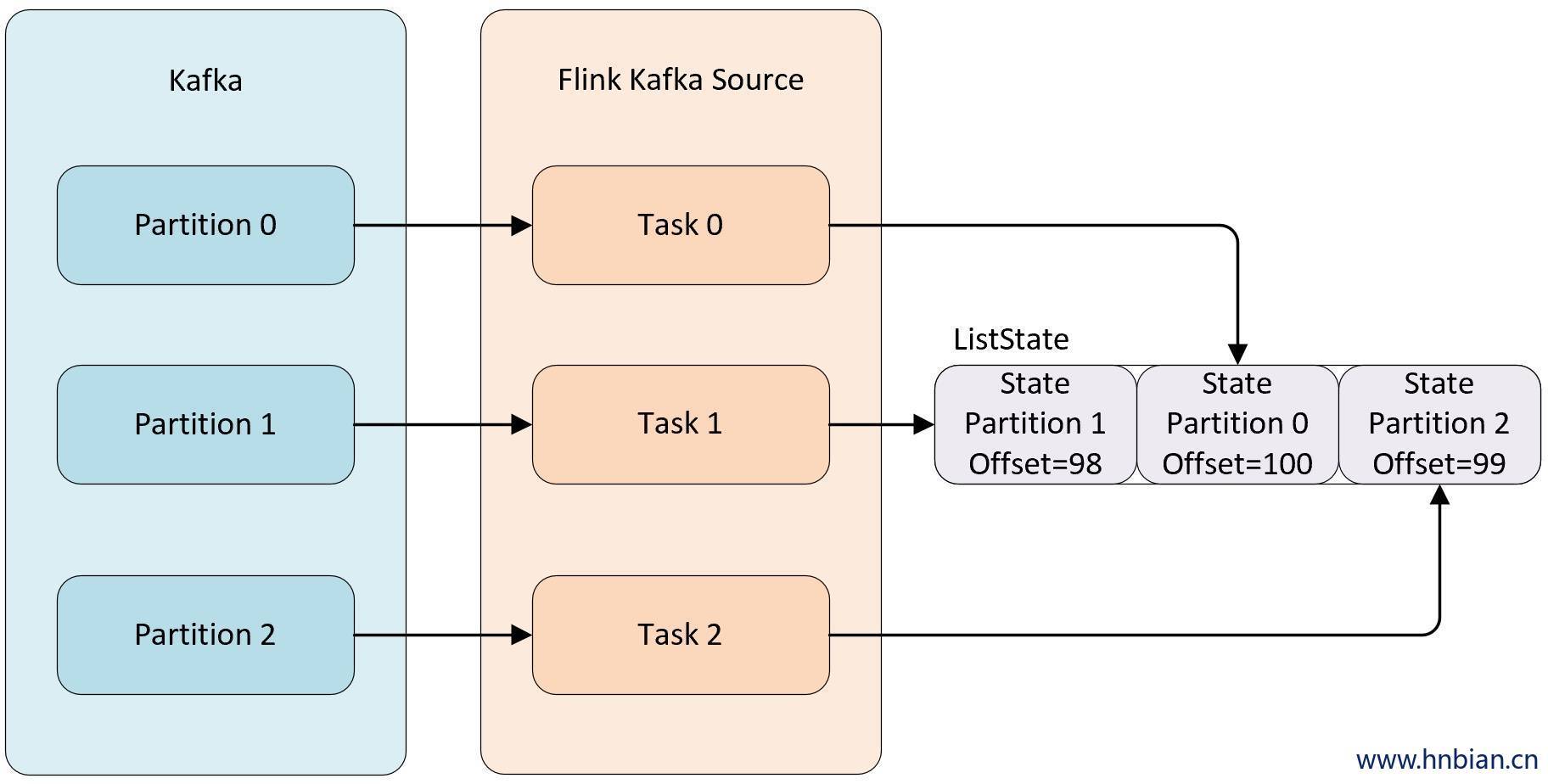
例如当消费 kafka 数据的 Kafka Source 并行度为 3 时,默认每个并行度都是从一个 Kafka 的 topic 的某个分区中消费数据,而每个 kafka Source 为了保证在极端情况下也不丢失数据,就不能将 partition 对应的 offset 保存到默认的 zookeeper 中,而是需要将这些数据保存在状态中,自己来维护这部分数据。当并行度发生调整时,需要在 Operator 的并行度上重新分配状态。
在流数据开发的大多数场景中,我们都不需要使用 Operator State ,Operator State 的实现主要是针对一些没有 Keyed 操作的 Source 和 Sink 而设计的。
Operator State 的作用范围限定为算子任务。这意味着由同一并行任务所处理的所有数据都可以访问到相同的状态,状态对于同一任务而言是共享的。算子状态不能由相同或不同算子的另一个任务访问。
Flink 为算子状态提供三种基本数据结构:
列表状态( List state ):状态是一个 可序列化 对象的集合 List,彼此独立,方便在改变并发后进行状态的重新分派。 换句话说,这些对象是重新分配 non-Keyed State 的最细粒度。根据状态的不同访问方式,有如下两种重新分配的模式:
Even-split redistribution: 每个算子都保存一个列表形式的状态集合,整个状态由所有的列表拼接而成。当作业恢复或重新分配的时候,整个状态会按照算子的并发度进行均匀分配。 比如说,算子 A 的并发读为 1,包含两个元素 element1 和 element2,当并发读增加为 2 时,element1 会被分到并发 0 上,element2 则会被分到并发 1 上。
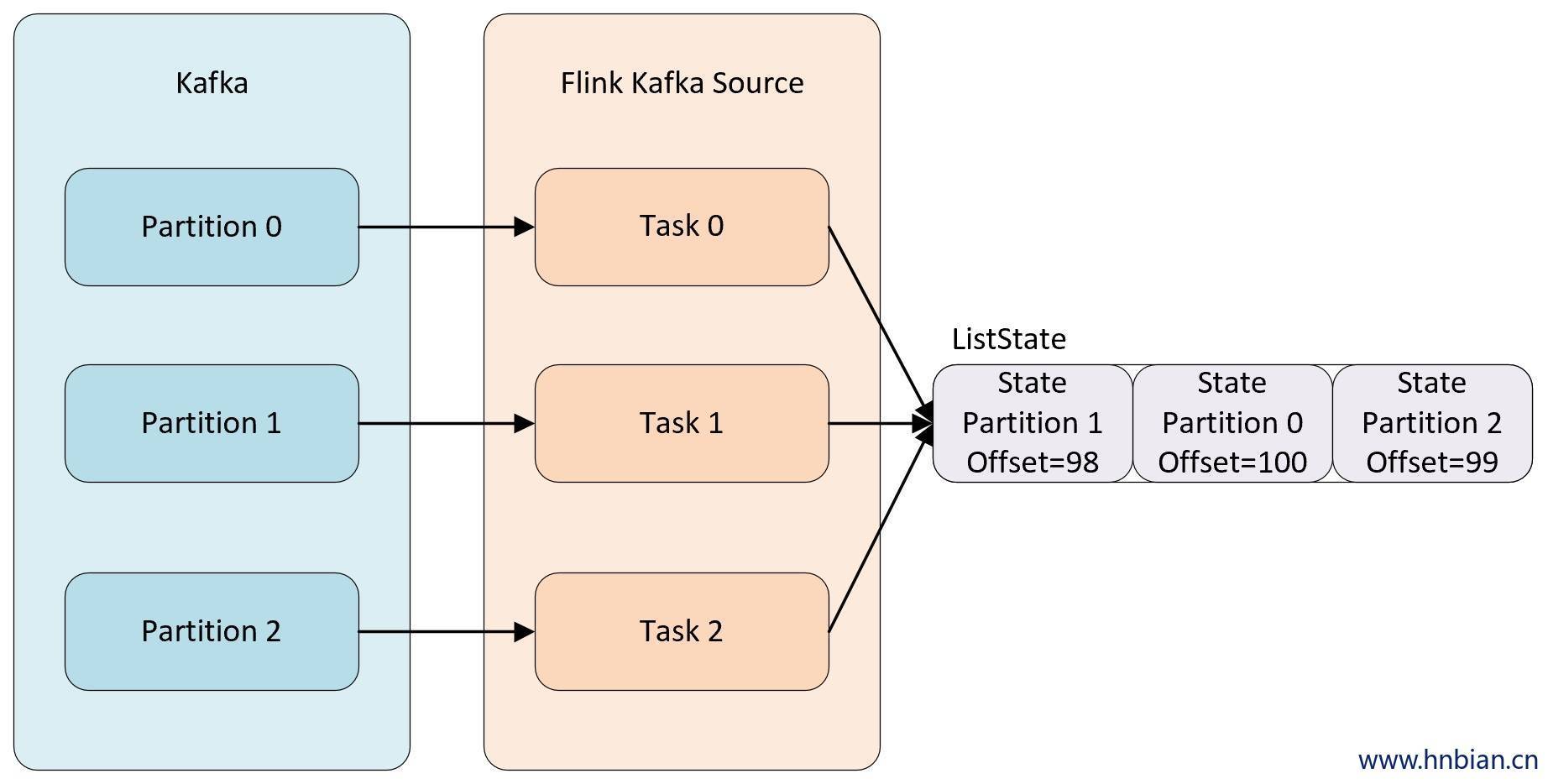
Union redistribution: 每个算子保存一个列表形式的状态集合。整个状态由所有的列表拼接而成。当作业恢复或重新分配时,每个算子都将获得所有的状态数据。Union redistribution 模式下 checkpoint metadata会存储每个operator 的 subTask 的offset信息。如果List State的基数较大时,不要使用这种方式的redistribution。因为容易引起OOM。
调用不同的获取状态对象的接口,会使用不同的状态分配算法。比如 getUnionListState(descriptor) 会使用 union redistribution 算法, 而 getListState(descriptor) 则简单的使用 even-split redistribution 算法。
当初始化好状态对象后,我们通过 isRestored() 方法判断是否从之前的故障中恢复回来,如果该方法返回 true 则表示从故障中进行恢复,会执行接下来的恢复逻辑。
广播状态( Broadcast state ):如果一个算子有多项任务,而它的每项任务状态又都相同,那么这种特殊情况最适合应用广播状态。
4. Keyed State 使用示例 4.1 ValueState
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 import com.hnbian.flink.common.Obj1 import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{ValueState , ValueStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector object TestValueState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Obj1 ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Obj1 (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toLong) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Obj1 , String ] = value.keyBy(_.id) value1 .process(new TestValueState ) .print("TestValueState" ) env.execute() } class TestValueState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ] val valueStateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor [Obj1 ]("objs" , Types .of[Obj1 ]) lazy val valueState: ValueState [Obj1 ] = getRuntimeContext.getState(valueStateDescriptor) override def processElement Obj1 , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]) = { val prev = valueState.value() if (null == prev){ valueState.update(value) }else { val obj1 = valueState.value() println(s"obj1.time=${obj1.time} ,value.time=${value.time} " ) if (obj1.time < value.time){ valueState.update(value) } } out.collect(value.name) } }
4.2 ListState
列表状态:ListState [T] 保存一个列表,列表里的元素的数据类型为 T
获取列表状态:ListState.get() 返回 Iterable[T]
添加单个元素到列表状态:ListState.add(value: T)
添加多个元素到列表状态:ListState.addAll(values: java.util.List[T])
添加多个元素更新列表状态的数据:ListState.update(values: java.util.List[T])
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import java.utilimport com.hnbian.flink.common.Obj1 import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{ListState , ListStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer object TestListState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Obj1 ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Obj1 (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toLong) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Obj1 , String ] = value.keyBy(_.id) value1 .process(new TestListState ) .print("TestListState" ) env.execute() } class TestListState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ] val listStateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor [Obj1 ]("objs" , Types .of[Obj1 ]) private lazy val listState: ListState [Obj1 ] = getRuntimeContext.getListState(listStateDescriptor) override def processElement Obj1 , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]) = { val iterable: util.Iterator [Obj1 ] = listState.get().iterator() val list:ListBuffer [Obj1 ] = new ListBuffer [Obj1 ] while (iterable.hasNext){ list.append(iterable.next()) } list.append(value) if (list.size > 2 ){ list.remove(0 ) } import scala.collection.JavaConverters .seqAsJavaListConverter val javaList: util.List [Obj1 ] = list.toList.asJava listState.update(javaList) out.collect(list.toString()) } }
4.3 MapState
映射状态:MapState [K, V] 保存 Key-Value 对
获取数据:MapState.get(key: K)
保存数据:MapState.put(key: K, value: V)
检查是否包含某个 key:MapState.contains(key: K)
移除某个key对应的数据:MapState.remove(key: K)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import com.hnbian.flink.common.Obj1 import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{MapState , MapStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer object TestMapState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Obj1 ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Obj1 (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toLong) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Obj1 , String ] = value.keyBy(_.id) value1 .process(new TestMapState ) .print("TestMapState" ) env.execute() } class TestMapState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ] private val mapStateDescriptor = new MapStateDescriptor [String ,ListBuffer [Obj1 ]]("objs" , Types .of[String ], Types .of[ListBuffer [Obj1 ]]) private lazy val mapState: MapState [String , ListBuffer [Obj1 ]] = getRuntimeContext.getMapState(mapStateDescriptor) override def processElement Obj1 , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]): Unit = { if (mapState.contains(ctx.getCurrentKey)){ val list: ListBuffer [Obj1 ] = mapState.get(ctx.getCurrentKey) if (list.size >=2 ){ list.remove(0 ) list.append(value) mapState.put(ctx.getCurrentKey,list) }else { list.append(value) mapState.put(ctx.getCurrentKey,list) } }else { val list: ListBuffer [Obj1 ] = ListBuffer (value) mapState.put(ctx.getCurrentKey,list) } out.collect(mapState.values().toString) } }
4.4 ReducingState
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 import com.hnbian.flink.common.Obj1 import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{ReducingState , ReducingStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector object TestReducingState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Obj1 ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Obj1 (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toLong) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Obj1 , String ] = value.keyBy(_.id) value1 .process(new TestReducingState ) .print("TestReducingState" ) env.execute() } class TestReducingState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String ,Obj1 ,String ] private val reducingStateDescriptor = new ReducingStateDescriptor [Obj1 ]("biggerTime" , new Reduce ,Types .of[Obj1 ]) lazy private val reducingState: ReducingState [Obj1 ] = getRuntimeContext.getReducingState(reducingStateDescriptor) override def processElement Obj1 , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]): Unit = { reducingState.add(value) out.collect(reducingState.get().toString) } } class Reduce extends ReduceFunction [Obj1 ] override def reduce Obj1 , value2: Obj1 ): Obj1 = { if (value1.time > value2.time){ value1 }else { value2 } } }
4.5 AggregatingState
Aggregate 聚合操作的状态:AggregatingState [I, O]
获取数据:AggregatingState.get()
添加数据:AggregatingState.add(T)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import com.hnbian.flink.window.TumblingTimeWIndow .Record import com.hnbian.flink.window.function.AverageAccumulator import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.AggregateFunction import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{AggregatingState , AggregatingStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer object TestAggregatingState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Record ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Record (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toInt) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Record , String ] = value.keyBy(_.classId) value1 .process(new TestAggregatingState ) .print("TestListState" ) env.execute() } class TestAggregatingState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String ,Record ,(ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )] private val aggregatingStateDescriptor = new AggregatingStateDescriptor [Record , AverageAccumulator , (ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )]("agg" , new AgeAverageAggregateFunction ,Types .of[AverageAccumulator ]) lazy private val aggregatingState: AggregatingState [Record , (ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )] = getRuntimeContext.getAggregatingState(aggregatingStateDescriptor) override def processElement Record , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Record , (ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )]#Context , out: Collector [(ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )]): Unit = { aggregatingState.add(value) out.collect(aggregatingState.get()) } } class AgeAverageAggregateFunction extends AggregateFunction [Record , AverageAccumulator , (ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )] override def getResult AverageAccumulator ): (ArrayBuffer [Record ], Double )= { val avg = accumulator.sum./(accumulator.count.toDouble) (accumulator.records,avg) } override def merge AverageAccumulator , b: AverageAccumulator ): AverageAccumulator = { a.count += b.count a.sum += b.sum a.records.appendAll(b.records) a } override def createAccumulator AverageAccumulator = { new AverageAccumulator () } override def add Record , accumulator: AverageAccumulator ): AverageAccumulator = { accumulator.records.append(value) accumulator.sum += value.age accumulator.count+=1 accumulator } }
4.6 设置状态 TTL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 import java.utilimport com.hnbian.flink.common.Obj1 import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{ListState , ListStateDescriptor , StateTtlConfig }import org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._import org.apache.flink.util.Collector import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer object TestTTL extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) private val value: DataStream [Obj1 ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Obj1 (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 ).toLong) }) private val value1: KeyedStream [Obj1 , String ] = value.keyBy(_.id) value1 .process(new TestTTLValueState ) .print("TestTTL" ) env.execute() } class TestTTLValueState extends KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ] private val stateTtlConfig: StateTtlConfig = StateTtlConfig .newBuilder(Time .seconds(10 )) .setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig .UpdateType .OnReadAndWrite ) .setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig .StateVisibility .NeverReturnExpired ) .build() val listStateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor [Obj1 ]("objs" , Types .of[Obj1 ]) listStateDescriptor.enableTimeToLive(stateTtlConfig) private lazy val listState: ListState [Obj1 ] = getRuntimeContext.getListState(listStateDescriptor) override def processElement Obj1 , ctx: KeyedProcessFunction [String , Obj1 , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]) = { val iterable: util.Iterator [Obj1 ] = listState.get().iterator() val list:ListBuffer [Obj1 ] = new ListBuffer [Obj1 ] while (iterable.hasNext){ list.append(iterable.next()) } list.append(value) import scala.collection.JavaConverters .seqAsJavaListConverter val javaList: util.List [Obj1 ] = list.toList.asJava listState.update(javaList) out.collect(list.toString()) } }
5. Operator State 使用示例 要在自定义的函数或算子中使用Operator State,可以实现 CheckpointedFunction 接口,这是一个比较通用的接口,既可以管理 Operator State,也可以管理 Keyed State,灵活性比较强。
5.1 CheckpointedFunction 接口介绍 CheckpointedFunction 状态转换功能的核心接口,状态转换功能是指在各个流记录之间维护状态的功能。 虽然存在更多轻量级的接口作为各种类型状态的快捷方式,但此接口在管理键控状态和操作员状态方面提供了最大的灵活性。快捷方式部分说明了设置状态函数的常用轻量级方法,这些方法通常代替该接口表示的完整抽象使用。
当创建转换函数的并行实例进行分布式执行时,
会调用 initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext) 方法。
这个方法提供了对 FunctionInitializationContext 的访问,
而 FunctionInitializationContext 又提供了对 OperatorStateStore 和 KeyedStateStore 的访问。
OperatorStateStore 和 KeyedStateStore 是可以访问应存储状态的数据结构,
这使得 Flink 能够透明地管理和检查状态,
例如 org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState 或 org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListState。
每当检查点获取转换函数的状态快照时,都会调用snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext) 。 在此方法内部,函数通常会确保检查点数据结构(在初始化阶段中获得)是最新的,以获取快照。 给定的快照上下文可以访问检查点的元数据。另外,函数可以使用此方法作为挂钩来与外部系统进行刷新/提交/同步。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package org.apache.flink.streaming.api.checkpoint;import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RuntimeContext;import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.KeyedStateStore;import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.OperatorStateStore;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.FunctionInitializationContext;import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.FunctionSnapshotContext;public interface CheckpointedFunction { void snapshotState (FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception; void initializeState (FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception; }
进行 checkpoint 时会调用 snapshotState()。 用户自定义函数初始化时会调用 initializeState(),初始化包括第一次自定义函数初始化和从之前的 checkpoint 恢复。 因此 initializeState() 不仅是定义不同状态类型初始化的地方,也需要包括状态恢复的逻辑。
5.2 ListCheckpointed 接口介绍 ListCheckpointed 接口是 CheckpointedFunction 接口的一个简化版本,只支持均匀分布的ListState,并在还原时使用偶数拆分的重新分配方案。不支持全量广播的UnionListState,
该接口可以实现状态重分配功能,当operator的并行度发生更改时,会对状态进行重新分配。Operator State 的状态重新分配始终通过检查点,因此转换功能看起来像故障/恢复组合,其中恢复以不同的并行度进行。
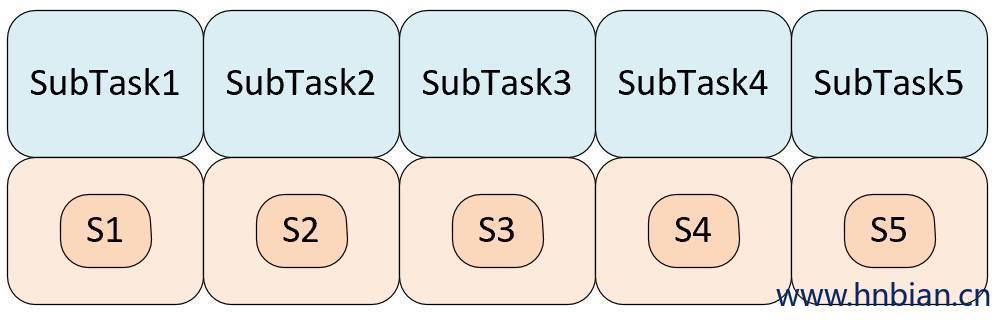
从概念上讲,检查点中的状态是并行转换函数实例返回的所有列表的串联列表。 从检查点还原时,该列表分为分配给每个并行功能实例的子列表。
下图说明了状态重新分配,该函数以并行性运行共有三个 subTask前两个并行实例返回带有两个状态元素的列表,第三个并行实例返回带有以个状态元素
使用 parallelism = 5 恢复检查点将产生以下状态分配:
使用 parallelism = 2 恢复检查点将产生以下状态分配:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package org.apache.flink.streaming.api.checkpoint;import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFunction;import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.OperatorStateStore;import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.List;@PublicEvolving public interface ListCheckpointed <T extends Serializable > { List<T> snapshotState (long checkpointId, long timestamp) throws Exception; void restoreState (List<T> state) throws Exception; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class CountingFunction <T> implements MapFunction <T, Tuple2<T, Long>>, ListCheckpointed<Long> { private long count; {@literal @}Override public List<Long> snapshotState (long checkpointId, long timestamp) { return Collections.singletonList(count); } {@literal @}Override public void restoreState (List<Long> state) throws Exception { for (Long l : state) { count += l; } } {@literal @}Override public Tuple2<T, Long> map (T value) { count++; return new Tuple2 <>(value, count); } }
5.3 List state 使用示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 import java.langimport org.apache.flink.api.scala.createTypeInformationimport org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.{FunctionInitializationContext , FunctionSnapshotContext }import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.checkpoint.CheckpointedFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.{RichSourceFunction , SourceFunction }import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream , StreamExecutionEnvironment }import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer import scala.util.Random object TestListState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment env.setParallelism(1 ) import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.filesystem.FsStateBackend import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.CheckpointingMode import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.CheckpointConfig env.enableCheckpointing(5000 ) val stateBackend = new FsStateBackend ("file:///opt/flink-1.10.2/checkpoint" ,true ) env.setStateBackend(stateBackend) env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode .EXACTLY_ONCE ) env.getCheckpointConfig.setMinPauseBetweenCheckpoints(500 ) env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointTimeout(30 * 1000 ) env.getCheckpointConfig.setMaxConcurrentCheckpoints(1 ) env.getCheckpointConfig.enableExternalizedCheckpoints(CheckpointConfig .ExternalizedCheckpointCleanup .RETAIN_ON_CANCELLATION ) private val stream: DataStream [String ] = env.addSource(new WordDataSourceWithState ) stream.print("TestListState" ) env.execute() } class WordDataSourceWithState extends RichSourceFunction [String ] with CheckpointedFunction var isCancel:Boolean = _ val words = ArrayBuffer ("hadoop" , "spark" , "linux" , "flink" , "flume" , "oozie" , "kylin" ) var totalCount:BigInt = _ var random:Random = _ import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListState var listState: ListState [BigInt ] = null override def open Configuration ): Unit = { isCancel = false totalCount = 0 random = new Random } override def run SourceFunction .SourceContext [String ]): Unit = { while (!isCancel){ if (totalCount.intValue() % 10 == 0 ){ ctx.collect("primitive" ); }else { ctx.collect(words(random.nextInt(words.length))) } totalCount = totalCount+1 Thread .sleep(random.nextInt(3000 )) } } override def snapshotState FunctionSnapshotContext ): Unit = { listState.clear listState.add(totalCount) println(s"保存状态,totalCount=${totalCount} " ) } override def initializeState FunctionInitializationContext ): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListStateDescriptor import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation println("初始化状态" ) val totalCountListStateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor [BigInt ]("total_count" , TypeInformation .of(classOf[BigInt ])) listState = context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState(totalCountListStateDescriptor) val iterTotalCnt2: lang.Iterable [BigInt ] = listState.get val has = iterTotalCnt2.iterator().hasNext println(s"has=$has " ) println(s"context.isRestored()=${context.isRestored()} " ) if (context.isRestored()){ println("恢复数据" ) val iterTotalCnt: lang.Iterable [BigInt ] = listState.get import java.util val iterator: util.Iterator [BigInt ] = iterTotalCnt.iterator if (iterator.hasNext) { totalCount = iterator.next println(s"恢复数据,totalCount=${totalCount} " ) } } } override def cancel Unit = { isCancel = true } }
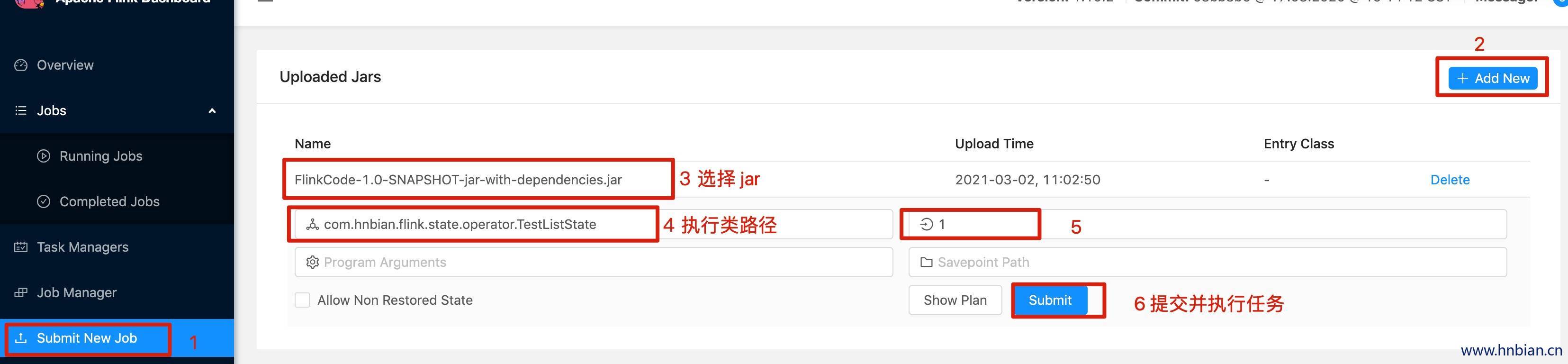
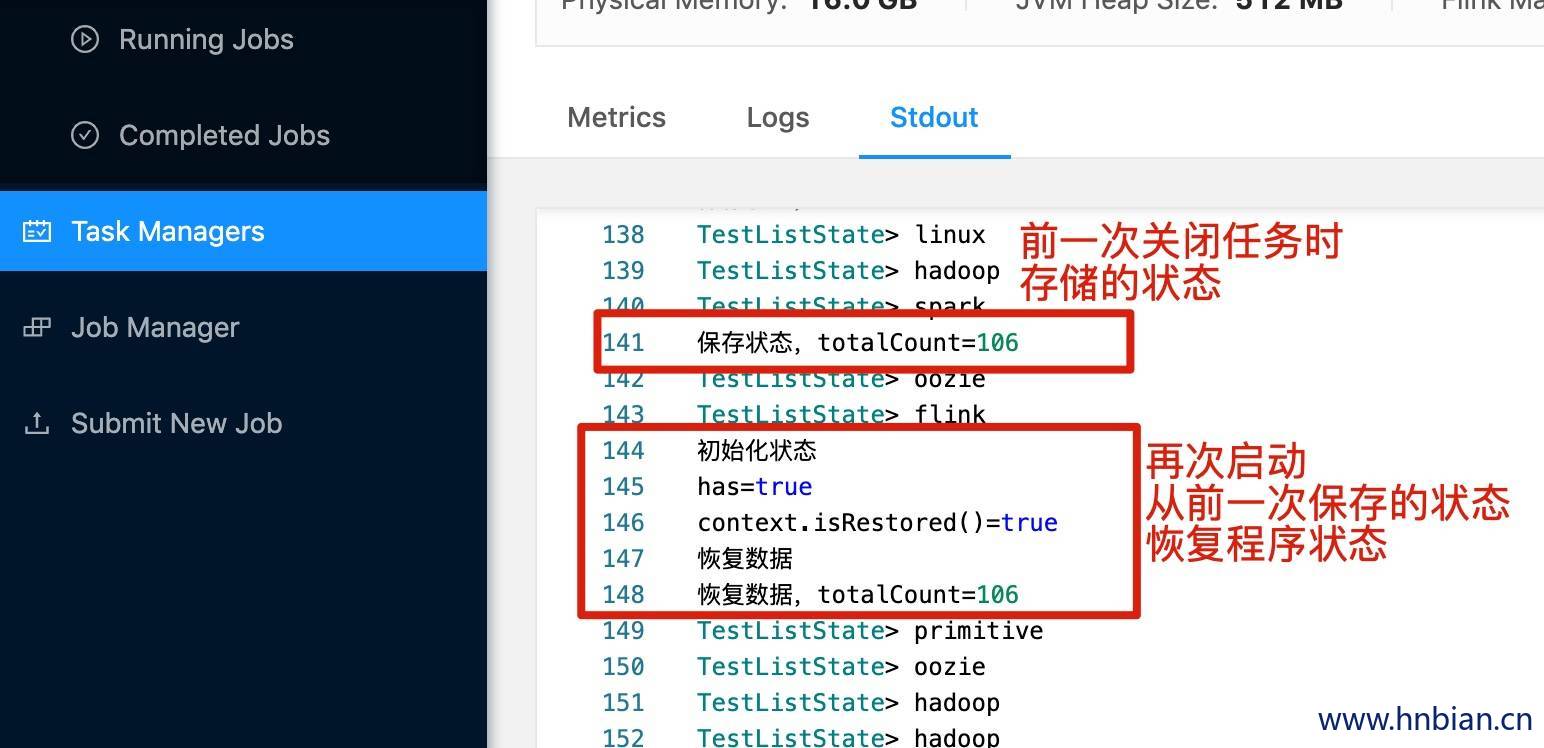
启动 Flink 集群,将代码打包提交任务到 flink 集群,然后查看结果
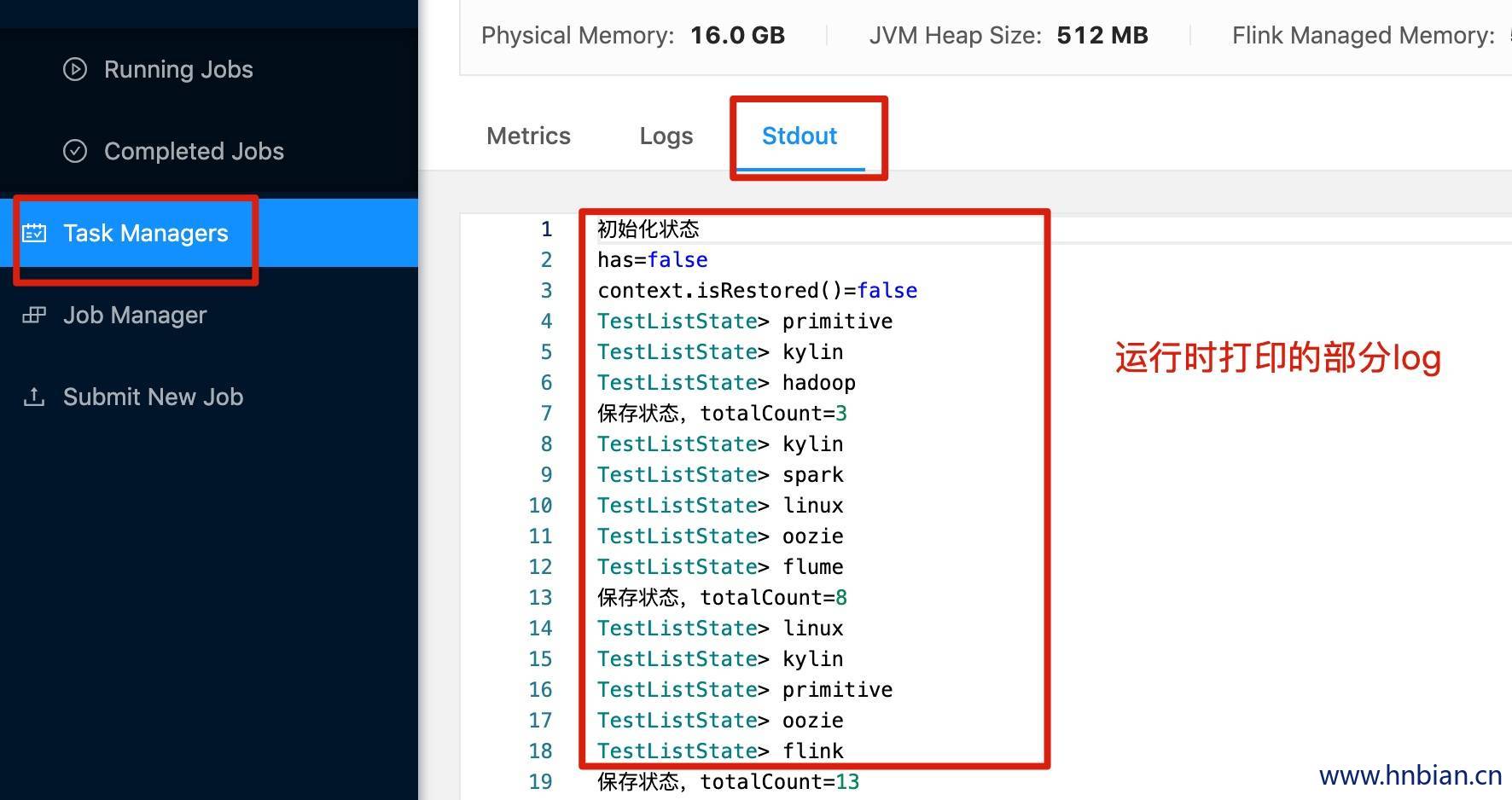
查看打印的日志
查看 checkpoint 保存的状态数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 hnbiandeMacBook-Pro:~ hnbian$ cd /opt/flink-1.10.2/checkpoint/9a4163a1d00b4ed51a4387c2bd341d72/ hnbiandeMacBook-Pro:9a4163a1d00b4ed51a4387c2bd341d72 hnbian$ pwd /opt/flink-1.10.2/checkpoint/9a4163a1d00b4ed51a4387c2bd341d72 hnbiandeMacBook-Pro:9a4163a1d00b4ed51a4387c2bd341d72 hnbian$ ll total 0 drwxr-xr-x 2 hnbian wheel 64B Mar 2 11:04 shared drwxr-xr-x 2 hnbian wheel 64B Mar 2 11:04 taskowned drwxr-xr-x 3 hnbian wheel 96B Mar 2 11:06 chk-32 hnbiandeMacBook-Pro:9a4163a1d00b4ed51a4387c2bd341d72 hnbian$ cd chk-32/ hnbiandeMacBook-Pro:chk-32 hnbian$ ll total 8 -rw-r--r-- 1 hnbian wheel 903B Mar 2 11:06 _metadata
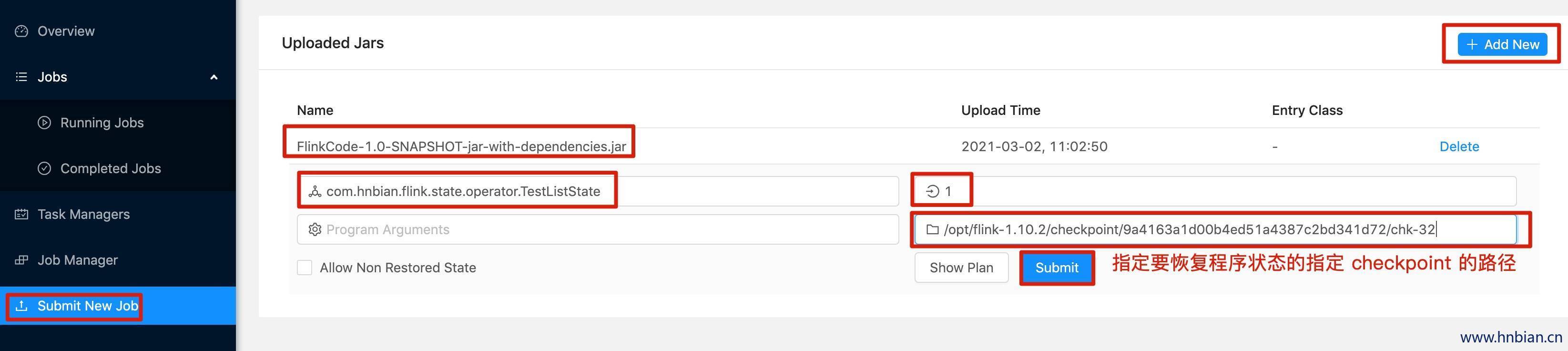
关闭程序,并从 checkpoint 恢复程序状态
5.4 Broadcast state 使用示例 Broadcast State(广播状态),可以将一个流中的数据广播到下游算子的每个 task中,使得这些数据再所有的 task 中共享,比如用于配置的一些数据,通过Broadcast state,我们可以让下游的每一个task,配置保持一致,当配置有修改时也能够使用Broadcast State 对下游每个 task 中的相关配置进行变更。
Broadcast State比较适合这种场景,假设我们做一个规则匹配事件处理系统,规则是一个低吞吐的流、而事件是一个高吞吐的流。我们可以将规则以Broadcast State的方式发送到下游每一个任务中,然后当有事件需要处理时,可以从广播中读取之前的规则,进行处理。
Broadcast State是一个Map结构,它比较适合于一个broadcast stream、另外一个不是broadcast stream的两个流进行相关操作的场景。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import com.hnbian.flink.common.{Class , Student }import com.hnbian.flink.process. TestBroadcastProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{BroadcastState , MapStateDescriptor }import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.BasicTypeInfo import org.apache.flink.api.scala.createTypeInformationimport org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.BroadcastStream import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.co.BroadcastProcessFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream , StreamExecutionEnvironment }import org.apache.flink.util.Collector object TestBroadcastState extends App val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment .getExecutionEnvironment val stream1: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,9999 ) val stream2: DataStream [String ] = env.socketTextStream("localhost" ,8888 ) private val StudentStream : DataStream [Student ] = stream1 .map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Student (arr(0 ), arr(1 ), arr(2 )) }) val descriptor = new MapStateDescriptor [String , String ]("classInfo" , BasicTypeInfo .STRING_TYPE_INFO , BasicTypeInfo .STRING_TYPE_INFO ) val ClassStream : DataStream [Class ] = stream2.map(data => { val arr = data.split("," ) Class (arr(0 ), arr(1 )) }) val ClassBradoStream : BroadcastStream [Class ] = ClassStream .broadcast(descriptor) StudentStream .connect(ClassBradoStream ) .process(new CustomBroadcastState ) .print("CustomBroadcastState" ) env.execute() } class CustomBroadcastState extends BroadcastProcessFunction [Student ,Class ,String ] private val mapStateDescriptor = new MapStateDescriptor [String ,String ]("maps" , Types .of[String ], Types .of[String ]) override def processElement Student , ctx: BroadcastProcessFunction [Student , Class , String ]#ReadOnlyContext , out: Collector [String ]): Unit = { val classInfo = ctx.getBroadcastState(TestBroadcastProcessFunction .descriptor) val className: String = classInfo.get(value.classId) out.collect(s"stuId:${value.id} stuName:${value.name} stuClassName:${className} " ) } override def processBroadcastElement Class , ctx: BroadcastProcessFunction [Student , Class , String ]#Context , out: Collector [String ]): Unit = { val classInfo: BroadcastState [String , String ] = ctx.getBroadcastState(mapStateDescriptor) println("更新状态" ) classInfo.put(value.id,value.name) } }